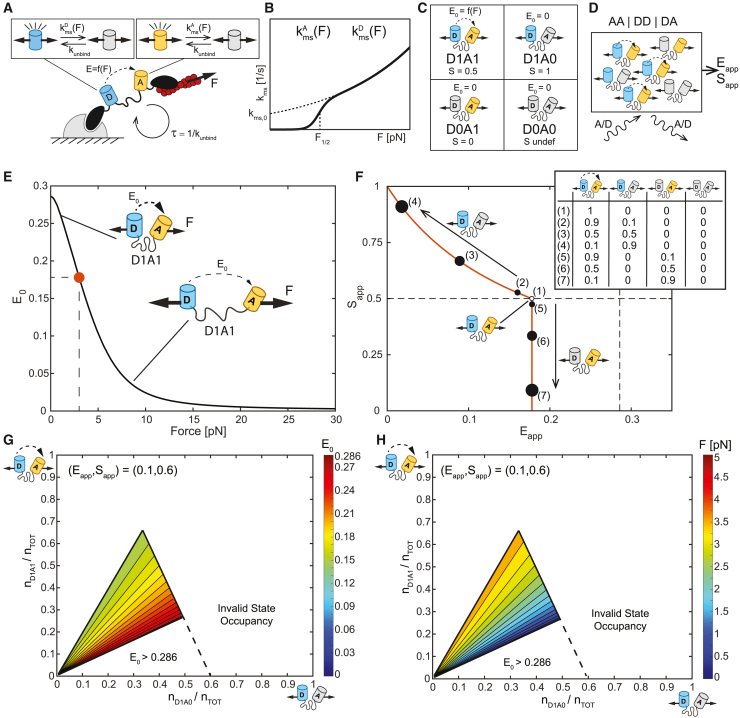
Figure 1.
Framework for FP mechanical switching in FRET-based MTSs
(A and B) (A) Model of FP mechanical switching in MTSs. MTSs are subject to dynamic loading parameterized by a load magnitude and a characteristic load duration , which is governed by unbinding from the loading source with rate constant . Donor and acceptor FPs are in the line of loading and undergo FP mechanical switching with force-dependent rate constants and . and have the same functional form, shown in (B), but different parameters.
(C) Four possible MTS states based on the status of the donor and acceptor FP. For each state, the FRET efficiency, , and FP stoichiometry, , are indicated.
(D) Schematic of 3-channel FRET measurements of a simulated population of MTSs.
(E) FRET efficiency-force calibration, , for an MTS in the D1A1 state, with dot indicating of 3 pN.
(F) Plot of versus containing the (, ) curve for MTS populations subject to constant loading at magnitude of 3 pN for cases of acceptor-only mechanical switching (varying amounts of D1A1 and D1A0 states) or donor-only mechanical switching (varying amounts of D1A1 and D0A1 states). The fraction of sensors in each state is indicated in the key.
(G) Contour plot of on the (fraction of sensors in D1A0 state, fraction of sensors in D1A1 state) plane demonstrating all values consistent with the single point (, ) of (0.1, 0.6). White indicates regions with invalid state occupancies and/or values.
(H) Corresponding contour plot of using the calibration in (E). Levels are in increments of 0.01 for (F) and 0.025 for (H).
The plots in (F)–(H) relate to Equations 3 and 4.
See also Note S1 and Figures S1–S4.