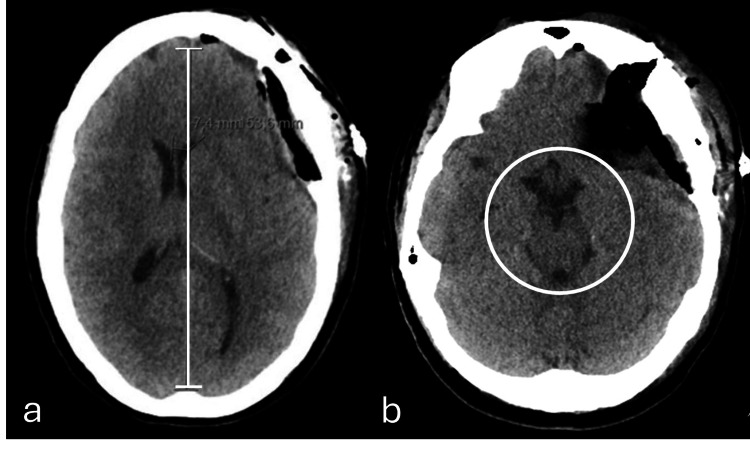
Figure 2. Axial plane of brain computed tomography obtained (a) post-meningioma resection (immediate post-operative phase) and (b) 24 hours post-resection without significant parenchymal changes.
(a) Signs of left fronto-temporal craniotomy associated with cranioplasty material (bone cement), covering a large part of the craniectomy area. It is also defined, underlying the craniotomy, as heterogeneous density material from the surgical duraplasty with small gaseous component (related to recent surgery) without significant hemorrhagic component. This material causes mass effect, with slight deformation of the adjacent parenchyma and ipsilateral ventricle, with 7 mm midline deviation of the midline structures to the right, but without significant subfalcine or uncal hernia. (b) The expansive effect exerted by these changes is unchanged, with persisting bihemispheric sulcal effacement and midline deviation of the structures to the right with attenuation of the suprasellar and perimesencephalic, which is associated with molding of the midbrain (white circle), without evident worsening compared to the prior (a) examination.