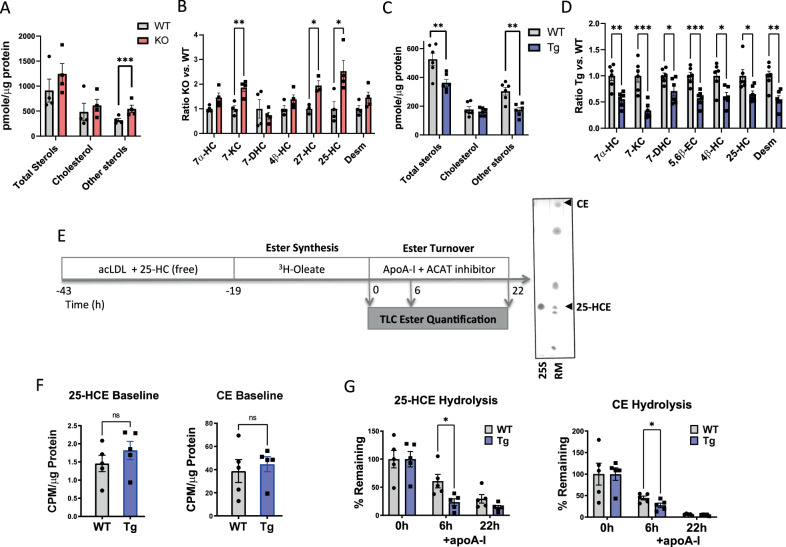
Fig. 5. LDAH mobilizes oxysterol stores.
A–D PM isolated from LDAH-Tg (Tg) and LDAH-KO (KO) mice and their respective WT controls were treated with oxLDL (50 μg/ml) for 48 h and lipid extracts were analyzed for sterols using LC-MS/MS (n = 4-6 independent samples). A Levels of total sterols, cholesterol, and oxysterols and (B) relative levels of the main oxysterol species identified in LDAH-KO PM (red bars) with respect to WT control (gray bars) PM (n = 4). C Levels of total sterols, cholesterol and oxysterols and (D) relative levels of the main oxysterol species identified in LDAH-Tg (blue bars) with respect to WT (gray bars) control PM (n = 6). 7α-HC = 7α-Hydroxycholesterol; 7-KC = 7-ketocholesterol; 5,6ß-EC = 5,6ß-Epoxycholesterol; 4ß-HC = 4ß-hydroxycholesterol; 25-HC = 25-hydroxycholesterol; 27-HC = 27-hydroxycholesterol; Desm= desmosterol. E Design of trafficking experiments to determine the rates of esterification and ester hydrolysis of cholesterol and 25-HC. Purified 25-HC oleate (25 S) and a TLC standard reference mixture (RM) were used to identify the 25-HCE and CE bands in TLC analysis. F 25-HC ester (25-HCE) and cholesterol ester (CE) levels after a pulse with 3H-oleate (baseline)(n = 5). G 25-HC and CE levels following chase with apoA-I (hydrolysis) (n = 5) Gray bars in F and G represent WT PM and blue bars correspond to LDAH-Tg PM. All bars represent mean ± SEM of independent samples. 25-HC in (D) total sterols in panel A and CE in panel F were analyzed using two-tailed Mann-Whitney U test. All other comparisons were performed using two-tailed unpaired t-test. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.