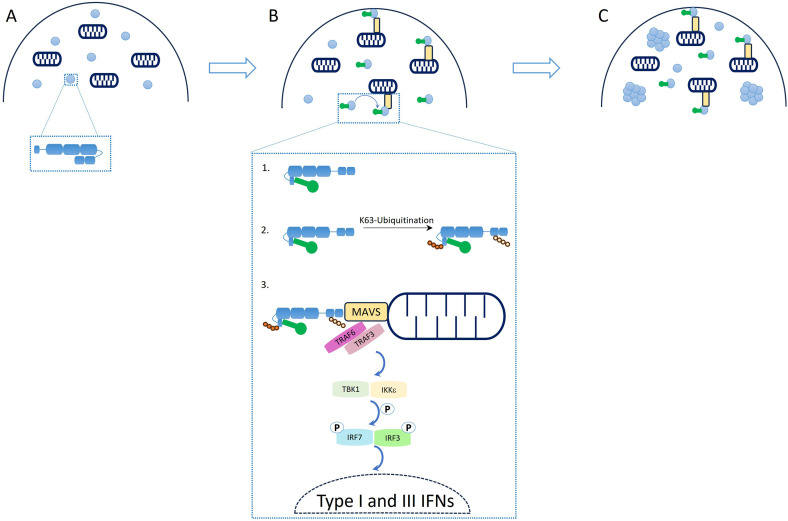
Figure 2.
Schematic representation of RIG-I's regulatory mechanisms controlling antiviral response. (a) Auto-repressed state of RIG-I with CARD domains buried in the helicase core. (b) IFNs activation cascade triggered by RNA binding: (b1) schematic representation of RNA binding to RIG-I and CARD release to solution; (b2) RIG-I's K63-linked ubiquitination mediated by several E3 ligases; (b3) downstream signaling cascade triggered by RIG-I induced MAVS oligomerization. (c) Formation of signaling-unrelated cytosolic aggregates of RIG-I. Figure is adapted from publication “A rapid RIG-I signaling relay mediates efficient antiviral response” 28 with permission from Elsevier. CARDs: caspase activation and recruitment domains; IFNs: interferons; RIG-I: retinoic acid-inducible gene I.