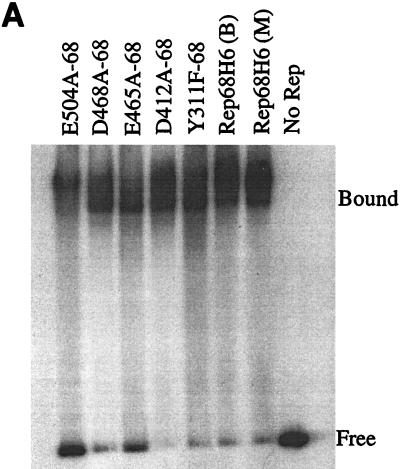
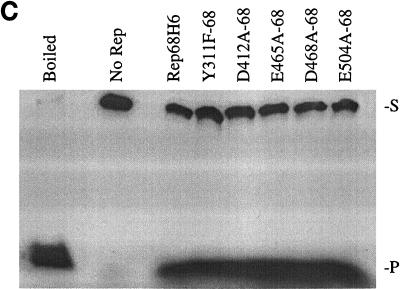
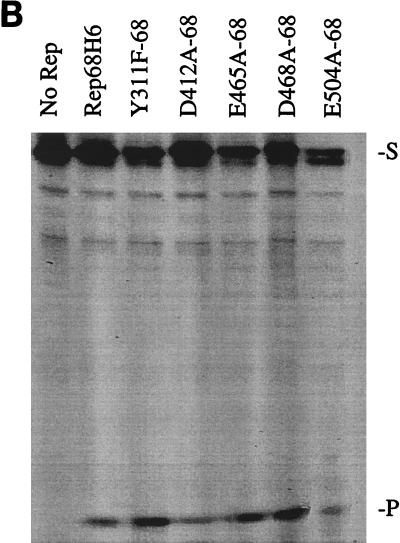
FIG. 5.
In vitro biochemical analyses of His-tagged Rep68 proteins. (A) Gel mobility shift assay of mutant and wt Rep68H6 proteins expressed in E. coli. Standard binding reaction mixtures contained 0.5 nM 32P-labeled AAV TR hairpin DNA (32P-TR) and 6 nM purified Rep68 protein containing the indicated mutation. Reactions were carried out in standard binding reaction buffer (see Materials and Methods) at 25°C for 30 min, and products were resolved on nondenaturing 5% polyacrylamide gels. Mutant and Rep68H6 (B) proteins were purified by one passage over nickel columns (batch) while Rep68H6 (M) was further purified by passage over a Mono Q column. (B) Terminal resolution by His-tagged Rep68 proteins. Standard trs endonuclease assays contained 0.5 nM 32P-TR substrate and 5 nM His-tagged protein. Nicking reactions were performed in standard nicking buffer (see Materials and Methods) for 60 min at 37°C, followed by protease K digestion and phenol-chloroform extraction, and products were resolved on denaturing polyacrylamide sequencing gels. Substrate (S) and cleavage products (P) are indicated. (C) Standard helicase reactions were performed at 37°C for 60 min in nicking buffer containing 0.5 nM substrate (M13/24) and 6 nM protein, and products were resolved on 5% nondenaturing polyacrylamide gels. Substrate (S) and released product (P) are indicated. Boiled, positive control. In all of the assays described for Fig. 5, E504A-68 required 50-fold more protein to achieve the level of activity shown.