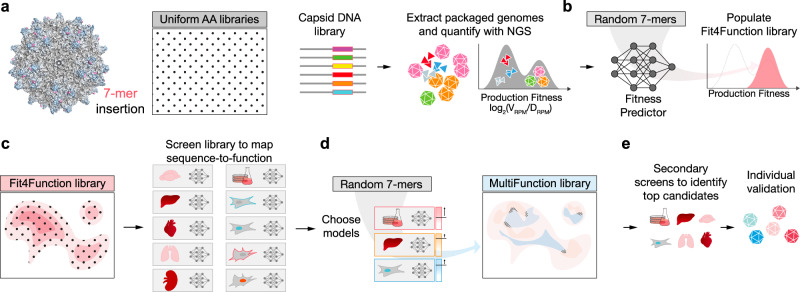
Fig. 1. Systematic multi-trait protein optimization paradigm.
a An insertion-modified AAV library that uniformly samples the 7-mer sequence space (1.28 billion possible variants) is designed and used to produce AAV particles. Variant production fitness is measured via Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS) of nuclease-resistant Cap-containing genomes (VRPM) relative to the number of genomes in the DNA library (DRPM). b The production fitness data is used to train a sequence-to-production-fitness ML model that is then used to design the Fit4Function library, which uniformly and exclusively samples the production-fit sequence space. c The Fit4Function library can be screened in vitro or in vivo for functions of interest, and the data are used to derive ML models that predict these functions from random 7-mer sequences. d The production fitness and functional fitness models are used in combination to populate MultiFunction libraries consisting of variants predicted to perform well across the desired traits (see checkered areas that represent the overlap between the functional sequence spaces of interest). e The MultiFunction AAV libraries are produced and screened for all functions of interest. The top-performing variants are then individually validated.