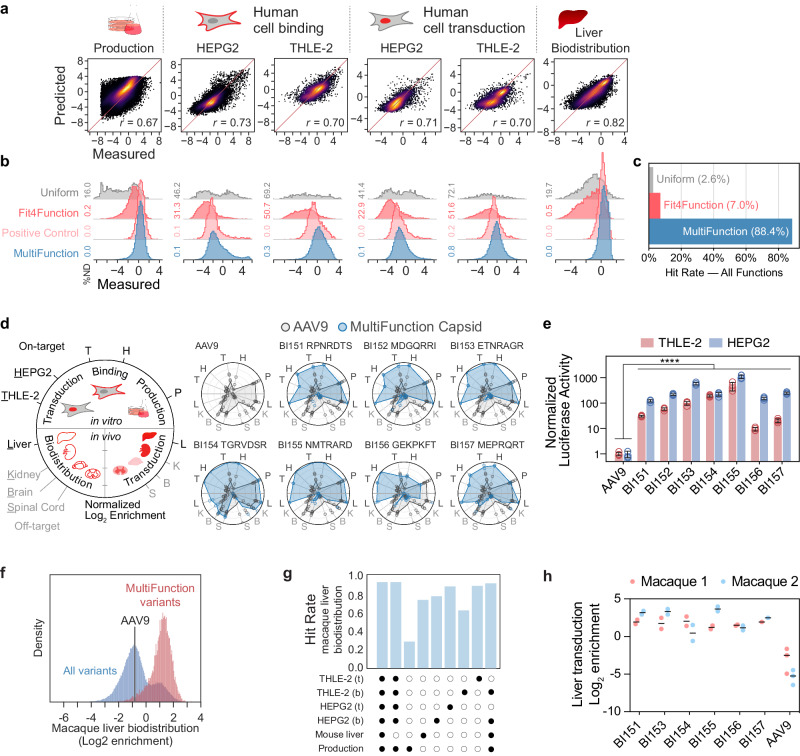
Fig. 4. Liver-targeted MultiFunction library design, validation in human cells and mice, and translation to macaque.
a The Pearson correlation of measured versus predicted enrichment are shown for production fitness and hepatocyte-targeting assays. b The enrichment distributions are shown across variants sampled from the Uniform, Fit4Function, Positive Control (Fit4Function variants satisfying the six conditions), and MultiFunction libraries. The histograms are density-normalized, including non-detected variants (ND). c The hit rates are shown for variants satisfying the six conditions in each listed variant set. d The on-target and off-target measurements for capsids BI151–157 and AAV9 in the MultiFunction library pool are shown as log2 enrichments of the selected capsid (two codon replicates) as compared to AAV9 (four codon replicates). The measured enrichment was linearly normalized according to the maximum and minimum values for each assay. Individual replicates are plotted as points. The average normalized enrichments across replicates are plotted as polygon vertices. e HEPG2 and THLE-2 transduction were assessed 24 h post-transduction at 3000 vg/cell using a luciferase assay (n = 4 transduction replicates per group, mean ± s.d., ****p < 1e−4, unpaired, one-sided t-tests on log-transformed values, and Bonferroni corrected for multiple hypotheses). The measurements were normalized to AAV9. f A 100K variant Fit4Function library was injected intravenously into a cynomolgus macaque and the vector genome distribution was assessed four hours later. Variants predicted to meet all six trait conditions were highly enriched in the cynomolgus macaque liver (biodistribution). The density plot shows the distribution of variants normalized to the sum of counts for each indicated set of variants. g The fraction of the indicated MultiFunction variants enriched in the cynomolgus macaque liver (defined as at least two-fold log2 enrichment greater than that of AAV9) are shown for each combination of predicted traits. Binding and transduction are indicated by ‘b’ and ‘t’, respectively. h The rhesus macaque liver transduction efficiency, measured by transcript levels 4-weeks post-administration, for the MultiFunction variants are shown (n = 2 rhesus macaques). Each variant was represented by two codon replicates while AAV9 was represented by three codon replicates. Source data are provided in a Source Data file.