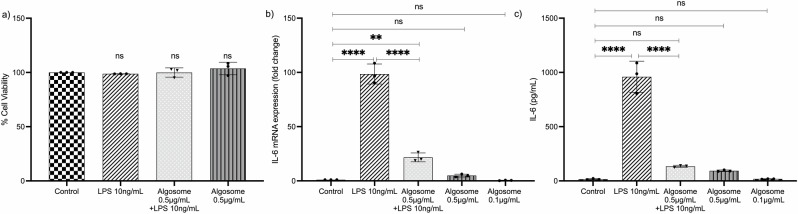
Fig. 7. Anti-inflammatory effect of nanoalgosomes in immune-responsive cells.
a Cell viability after exposure with LPS (10 ng/mL) and nanoalgosomes (0.5 µg/mL) for 24 h, in THP-1 cells. By one-way ANOVA statistical test, differences of treated cells were not statistically significant (ns) when compared with the control (p > 0.9). b Real-time PCR quantification of IL-6 mRNA relative levels after exposure with LPS (10 ng/mL) and nanoalgosomes (0.5 µg/mL) for 24 h, in THP-1 cells. c ELISA results of IL-6 induction after exposure with LPS (10 ng/mL) and nanoalgosomes (0.5 µg/mL) for 24 h, in THP-1 cells. One-way ANOVA statistical test was used to assess the statistical significance of the differences: Control vs LPS (10 ng/mL), LPS (10 ng/mL) vs Algosomes (0.5 µg/mL) + LPS (10 ng/mL), ****p < 0.0001; Control vs Algosomes (0.5 µg/mL) + LPS (10 ng/mL), **p < 0.01; Control vs Algosomes (0.5 µg/mL) are not statistically significant (ns, p > 0.9); Control vs Algosomes (0.1 µg/mL) are ns (p > 0.9). Representative results of three independent biological replicates (n = 3 biologically independent samples).