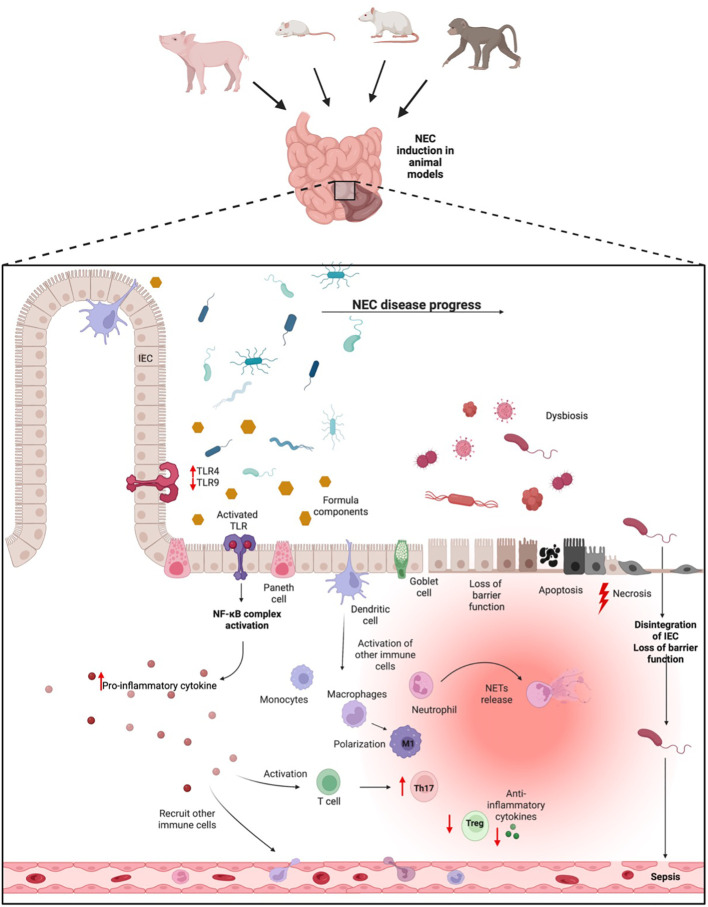
Figure 1.
NEC pathogenesis. In animal NEC models, NEC can be induced via different methods. In neonates that go on to develop NEC, a shift of the microbiome into a dysbiosis during the inflammatory progress takes place. This dysbiosis can be pronounced through formula feeding, which together might activate the TLR dependent inflammatory process. Activation of the TLR pathway leads to the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines, which in turn recruit immune cells from blood. Concurrently, the inflammatory process results in a loss of epithelial barrier function, apoptosis, and necrosis of intestinal tissue, resulting in potential bacterial penetration from the gut into the blood, ultimately leading to sepsis. IEC, Intestinal epithelial cells; TLR, Toll-like-receptor; Treg, T-regulatory cell; M1, pro-inflammatory Macrophages.