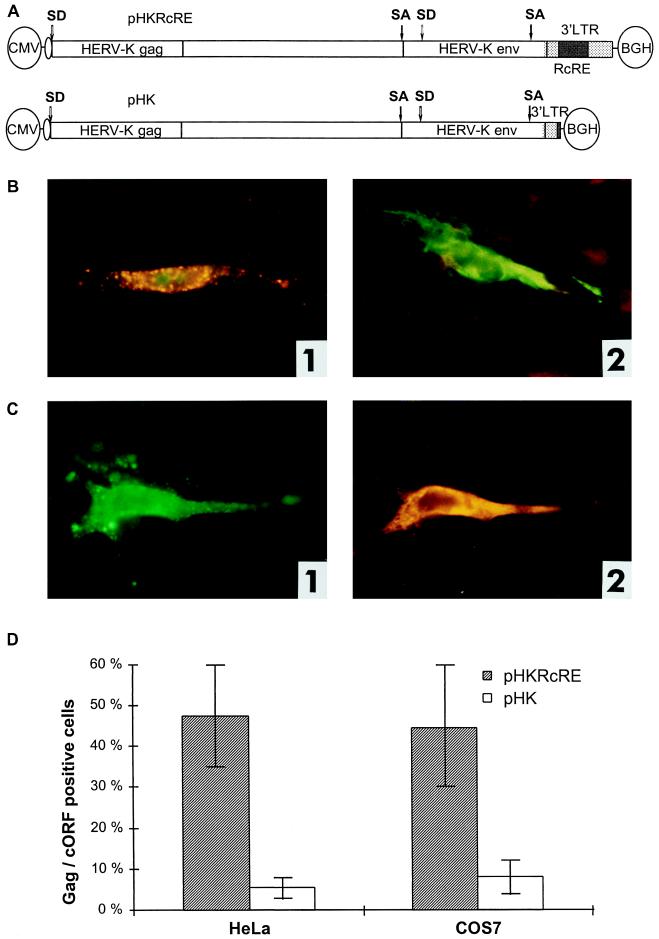
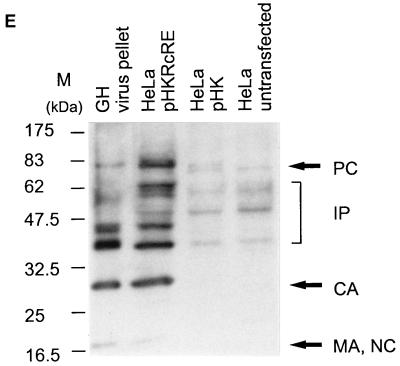
FIG. 4.
Posttranscriptional regulation of HTDV/HERV-K protein expression in full-length clones. (A) Expression vectors containing the complete HTDV/HERV-K genome with the exception of the 5′ LTR (starting with nt 1012): a cytomegalovirus (CMV) promoter was used to overcome the tissue specificity of HTDV/HERV-K LTRs. In the negative-control vector pHK, the RcRE and the HTDV/HERV-K termination signals were deleted. SA, splice acceptor; SD, splice donor; BGH, bovine growth hormone. (B) Transfections into HeLa cells. Panel 1, pHKRcRE: expression of HERV-K Gag (orange) and cORF (green); panel 2, pHK: expression of cORF (green). Staining was achieved with goat α-HERV-K Gag (panels 1 and 2) (orange) and with rabbit α-cORF (panels 1 and 2) (green). (C) Transfections of pHKRcRE into HeLa cells. Panel 1, expression of HERV-K Gag (green); panel 2, expression of Env (orange). Staining was performed with rabbit α-HERV-K Gag (panel 1) (green) and with goat α-HERV-K Env (panel 2) (orange). The same cell was photographed with an FITC filter to demonstrate Gag expression and with a Cy3 filter to show Env expression. (D) Quantification of Gag- and cORF- double-positive cells after transfection of pHKRcRE (hatched bars) or pHK (white bars) in HeLa (right) and COS7 (left) cells. cORF-positive cells were set as 100%. (E) Western blot analysis of Gag proteins in GH virus pellets (lane 1), in lysates of HeLa cells transfected with pHKRcRE (lane 2), or pHK (lane 3), and in lysates of untransfected HeLa cells (lane 4). PC, precursor; IP, intermediate proteins; CA, capsid; MA, matrix; NC, nucleocapsid. The positions of molecular mass markers (M) are indicated on the left.