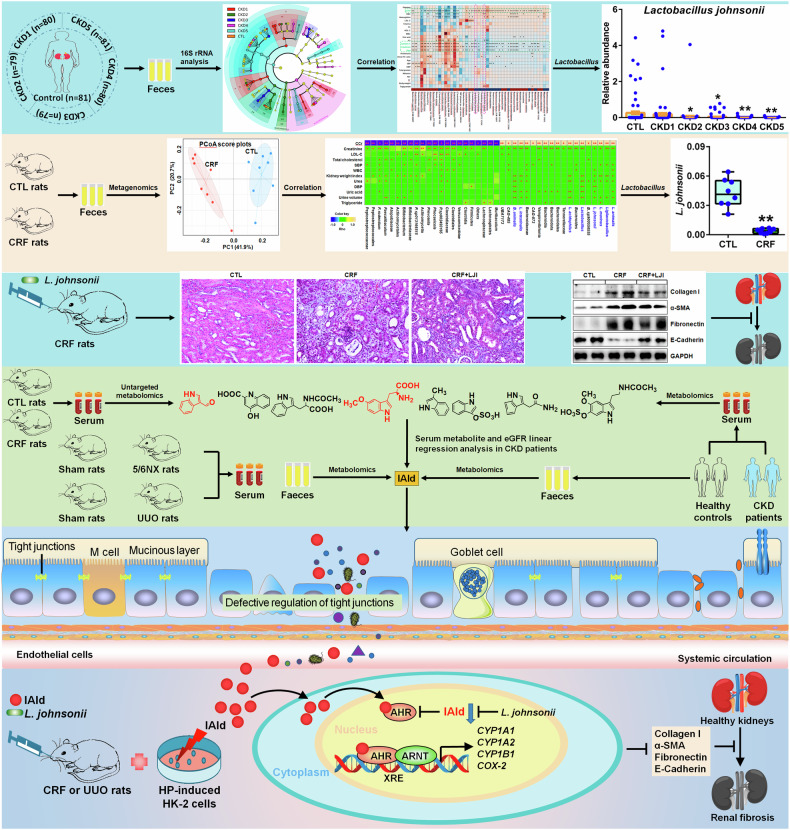
Fig. 10.
Renoprotective effects of L. johnsonii and molecular mechanism by AHR inhibition via IAld in CKD. An elongation chain Bacilli-Lactobacillales-Lactobacillaceae-Lactobacillus-L. johnsonii correlated with renal function decline in patients with CKD progression. Reduced L. johnsonii abundance was further observed in feces of CRF rats. L. johnsonii supplementation ameliorated renal injury and fibrosis. Eight metabolites were associated with kidney function. Serum IAld was further verified by rats induced by NX and UUO as well as CKD patients. IAld levels correlated with eGFR in CKD patients. IAld were produced by L. johnsonii via IpyA metabolic pathway. Treatment with IAld or L. johnsonii could ameliorate renal injury and fibrosis via AHR signaling pathway in CRF and/or UUO rats as well as HP-stimulated HK-2 cells. Parts of this schematic was created using Servier Medical Art, CC BY 4.0