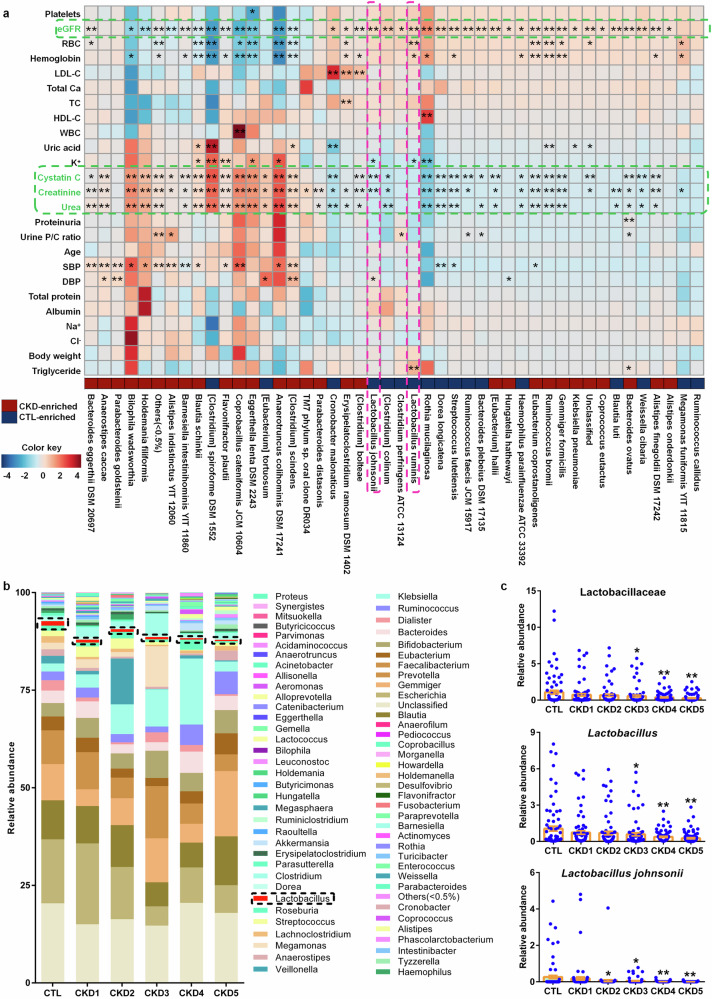
Fig. 2.
Decreased Lactobacillus abundance correlated with renal function decline in patients with CKD progression. a Associations between 46 significantly changed bacteria at the species level and 25 physiological and biochemical indexes in patients with CKD. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01. b Taxonomic distributions of bacteria at the genus level in controls and five stages of CKD. As shown by dashed box. c The relative abundances of Lactobacillaceae, Lactobacillus and Lactobacillus johnsonii in controls and five stages of CKD patients. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 compared with healthy controls (control, n = 80/group; CKD1, n = 81/group; CKD2, n = 80/group; CKD3, n = 79/group; CKD4, n = 79/group; CKD5, n = 81/group). Data are represented as mean ± SEM