Fig. 2|. 7-DHC suppresses ferroptosis.
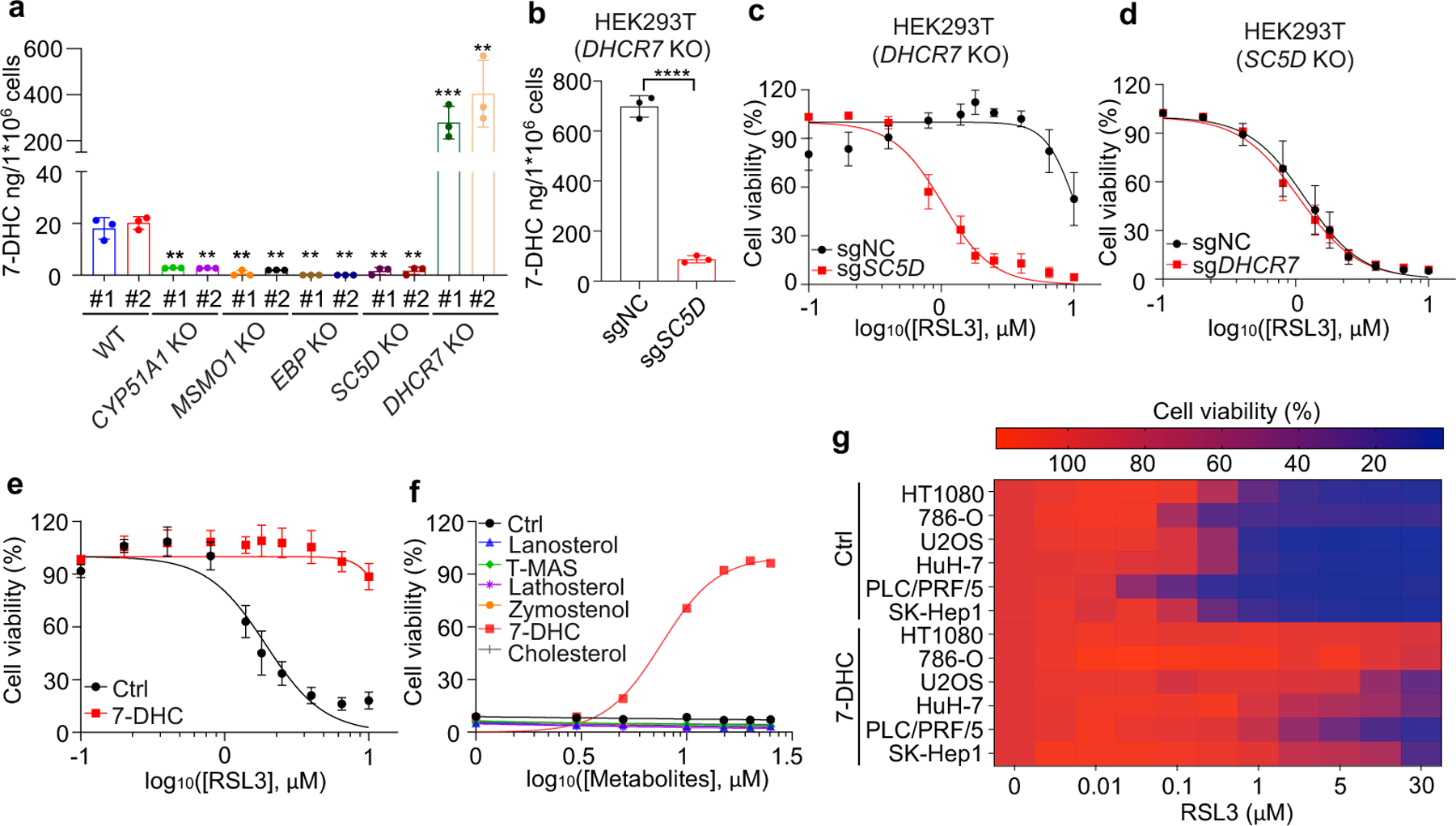
a, Levels of 7-DHC in WT and CYP51A1, MSMO1, EBP, SC5D, DHCR7 KO HEK293T cells b, Levels of 7-DHC in DHCR7 KO HEK293T cells expressing sgRNAs targeting negative control (sgNC) and SC5D (sgSC5D). c, Cell viability of DHCR7 KO HEK293T cells expressing sgRNAs targeting negative control (sgNC) and SC5D (sgSC5D) treated with RSL3 for 6–8 h. d, Cell viability of SC5D KO HEK293T cells expressing sgRNAs targeting negative control (sgNC) and DHCR7 (sgDHCR7) treated with RSL3 for 6–8 h. e, Cell viability of HEK293T cells treated with RSL3 for 6–8 h after pretreatment of 7-DHC (25 μM) for 24 h. f, Cell viability of HEK293T cells treated with RSL3 (5 μM) for 8 h after pretreatment of indicated concentrations of different sterols for 24 h. n=2 biological replicates. g, Heat map (data summarized from Extended Data Fig. 5a) depicting the dose-dependent toxicity of RSL3 in various human cancer cell lines, 7-DHC treatment vs. the ethanol control (Ctrl). Data are representative of two (a, b) and three (c-g) independent experiments. Data are mean ± s.d. of n=3 biological replicates (a-e), statistical analysis was performed using one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) (a) or unpaired two-tailed t-tests (b); **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; ****P < 0.0001
