Extended Data Fig. 1|. Identification of distal CB pathway including CYP51A1, MSMO1, EBP and SC5D as ferroptosis suppressors.
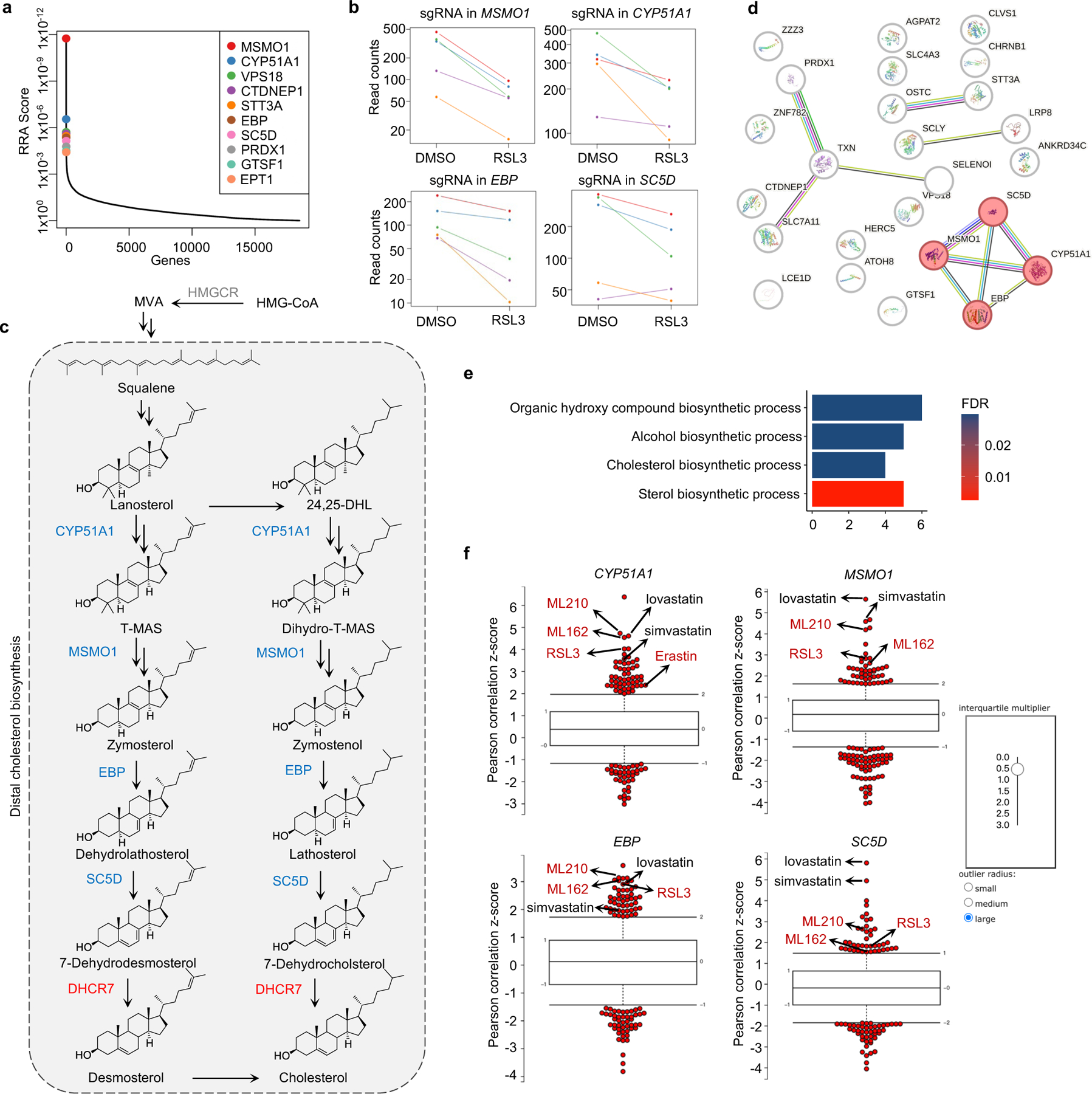
a, Integrative analysis of pooled CRISPR genetic screening using MAGeCK and identification of top candidate genes that were assigned with values generated from negative selection (anti-ferroptotic) by modified robust ranking aggregation (α-RRA) analysis. b, The normalized read counts of sgRNAs by CYP51A1, MSMO1, EBP and SC5D, generated by the MAGeCK-test module. n=5 sgRNAs per gene. c, Schema of the cholesterol pathway. Top screen hits are shown as red (pro-ferroptotic) or blue (anti-ferroptotic). d, The protein-protein interaction network was constructed using the STRING database to identify the top screening hits. e, GO analysis (conducted by https://string-db.org) evaluates global functional category enrichment of gene lists and indicates pathway-level pattern enrichment of cholesterol synthesis from the 50 top scoring genes. FDR are p-values corrected for multiple testing using the Benjamini–Hochberg procedure. f, CTRP analysis (conducted with https://portals.broadinstitute.org/ctrp.v2.1/) shows that the expression levels of CYP51A1, MSMO1, EBP and SC5D, positively correlate with their resistance to ferroptosis induced by the compounds (i.e. RSL3, ML162, ML210 and Erastin) in cancer cells. Plotted values are z-scored Pearson’s correlation coefficients with minima and maxima of the distributions; line, median; box, 25th–75th percentile; whiskers, expansion of outlier compounds (red dots) according to the interquartile multiplier (as shown in right).
