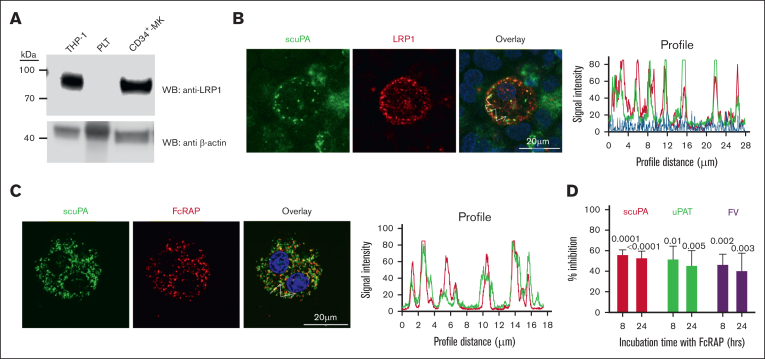
Figure 3.
LRP1 mediates uptake of scuPA, uPA-T, and FV by CD34+ MKs. (A) Representative WB, done as in Figure 1B, of lysates from THP-1 cell line as the positive control,43 donor-derived PLTs, and day-11 CD34+ MKs using anti-LRP light chain rabbit polyclonal antibody followed by HRP-conjugated goat anti-mouse antibody and HRP-conjugated anti–β-actin antibody as the loading control. (B) Confocal images of day-11 CD34+ MKs preloaded with scuPA (1 μM) for 24 hours and stained with mouse anti-uPA monoclonal antibody and anti-LRP1 rabbit polyclonal antibody followed by Alexa-488 goat anti-mouse polyclonal antibody (green) and Alexa-555 goat anti-rabbit polyclonal antibody (red) and DAPI nuclear stain (blue). (C) Confocal images of day-11 CD34+ MKs preloaded with Alexa-488 scuPA for 24 hours (green) followed by incubation with Alexa-555 FcRAP for 2 hours (red) on day 11. Scale bar is shown. Profile measurements in panels C-D are as in Figure 2A. (D) Inhibition of scuPA, uPA-T, and FV uptake by FcRAP. Day-11 CD34+ MKs were incubated with Alexa-488 scuPA or Alexa-488 uPAT or Alexa-568 FV (200 nM) in the absence or presence of FcRAP (2 μM) for either 8 or 24 hours, and MFI was measured using flow cytometry. Ordinate denotes percent uptake in the presence of FcRAP relative to in its absence. Mean ± 1 SD is shown. n = 3 to 4 independent studies. Data were analyzed using an ordinary 1-way ANOVA.