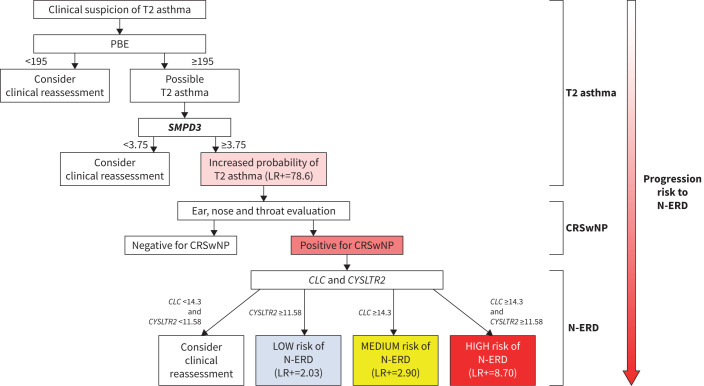
FIGURE 2.
Algorithm to assist in the diagnosis of T2 asthma and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug-exacerbated respiratory disease (N-ERD). The proposed algorithm starts with the peripheral blood eosinophil (PBE) counts as part of the T2 asthma diagnostic criteria. Our PBE cut-off (<195 cells·µL−1) can exclude the disease (likelihood ratio (LR)−=0.09). However, as other cut-offs exist (Global Initiative for Asthma guidelines [1]), negative results are left to the clinician's discretion (clinical reassessment is suggested). Also, obtaining airway samples for these patients would be advisable. If positive (≥195 cells·µL−1), the test should be confirmed. SMPD3 expression (cut-off >3.75 as per 2-ΔΔCt) in combination with PBE can accurately confirm the positive result (LR+=78.60), thus diagnosing T2 asthma. If the SMPD3 cut-off is <3.75, a negative result cannot be accurately given and a clinical reassessment should be considered. The diagnosis of chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyposis (CRSwNP) is assumed to be made by physicians (ear, nose and throat evaluation). If positive, the CLC and/or CYSLTR2 expression (considering the indicated cut-off points) can either indicate a low, medium or high risk for N-ERD. If both CLC and CYSLTR2 expression cut-offs are below their thresholds, a negative result cannot be accurately given and clinical reassessment should be undertaken. The boxes displaying a gradient of colour from light red (T2 asthma) to dark red (N-ERD) correspond to a possible disease progression. See text and table 6 for further details of cut-off points and LRs.