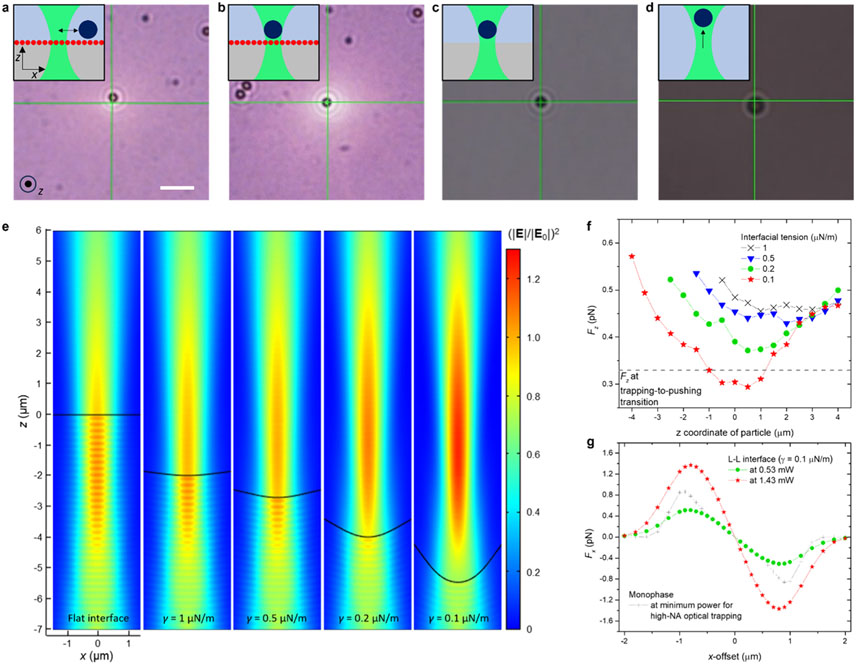
Figure 2.
Motion study of individual microparticles at liquid–liquid interfaces and deformation-based laser beam tuning at bare liquid–liquid interface. (a–d) Optical microscopic images of PS particles responding to a laser over the different type of interfaces: Au NP-loaded interface at optical powers of 0.24 mW (a) and 1.43 mW (b), bare liquid–liquid interface at 1.43 mW (c), and monophasic mixture of water and ethanol at 1.43 mW (d). Insets show system configurations and characteristic particle motion. Scale bar: 5 μm. (e) Intensity profiles of a Gaussian beam propagating through flat and deformed liquid–liquid interfaces, calculated with different interfacial tensions. The beam focal plane is fixed at z = 0. (f) Longitudinal optical force (Fz) profiles of a single PS particle (2 μm) with respect to z-offset of the particle from the beam center in interfacial systems with varying interfacial tensions at 1.43 mW. (g) Transverse optical force (Fx) profiles of the particle in the interfacial systems with respect to x-offset at 0.53 and 1.43 mW.