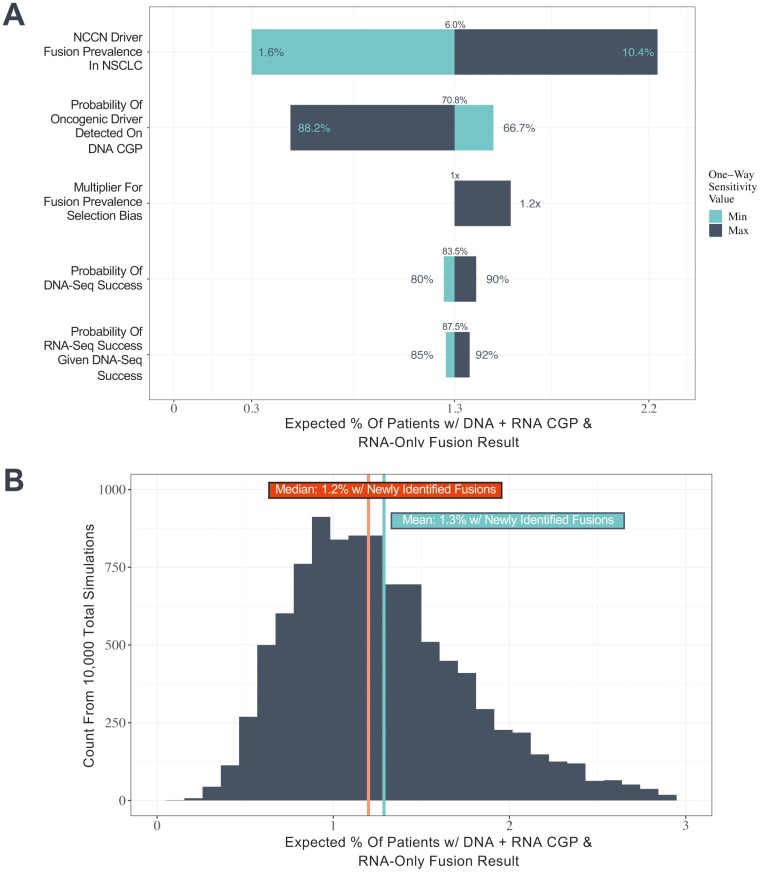
Figure 4.
1.3% of patients with NonSqNSCLC are expected to have an actionable fusion detected by RNA CGP that is not detected by DNA CGP. We conducted (A) one-way sensitivity analyses on key model parameters including the prevalence of oncogenic driver fusions in ALK, NTRK, RET, and ROS1 in NSCLC, the probability an oncogenic driver is detected in NSCLC using DNA CGP, the probability of successful DNA and RNA sequencing, and the potential selection bias for fusion-positive patients among those that do not have oncogenic driver alterations detected on DNA CGP and (B) a probabilistic sensitivity analysis incorporating parameter uncertainty jointly with mean and median estimates across 10 000 simulations indicated.