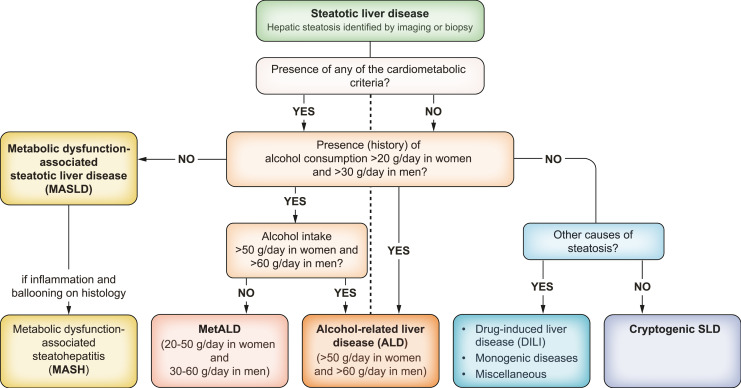
Fig. 1.
Flow-chart for SLD and its sub-categories [2]. SLD, diagnosed histologically or by imaging, has many potential aetiologies. MASLD is defined as the presence of hepatic steatosis in conjunction with (at least) one cardiometabolic risk factor and no other discernible cause. The quantity of alcohol intake, the drinking pattern, and the type of alcohol consumed should be assessed in all individuals with SLD using detailed medical history, psychometric instruments and/or validated biomarkers. ALD, alcohol-related liver disease; DILI, drug-induced liver disease; MASH, metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis; MASLD, metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease; MetALD, MASLD with moderate (increased) alcohol consumption; SLD, steatotic liver disease.