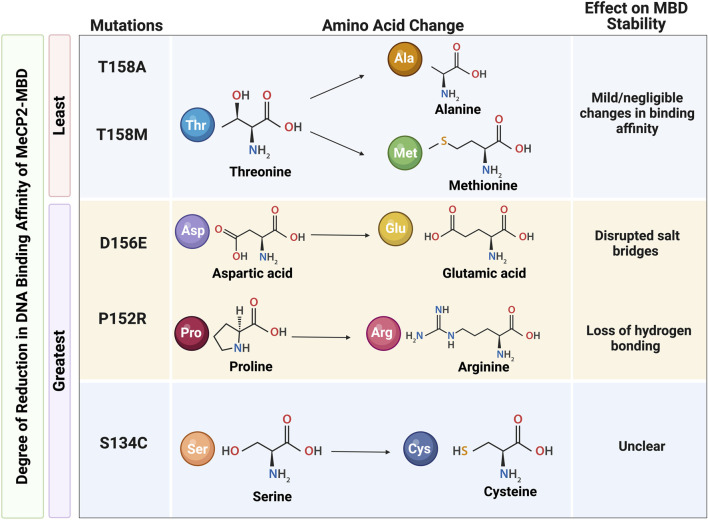
FIGURE 4.
The effect on MeCP2 methyl binding domain (MBD) stability due to mutations affecting the DNA binding affinity of MeCP2. A) The mildest reductions in MBD binding affinity are observed in the T158A and T158M mutations; the greatest reductions in MBD binding affinity are observed in the S134C, P152R, and D156E mutations. Reduced DNA binding affinity in the P152R and D156E mutations are explained by loss of hydrogen bonding and disrupted salt bridges, respectively. However, the reason for great reductions in the MBD binding affinity associated with the S134C mutation remains unclear. Information for this Figure are extracted from Kucukkal et al., 2015 and Yang et al., 2016 (Kucukkal et al., 2015; Yang et al., 2016). Illustration created in BioRender.com.