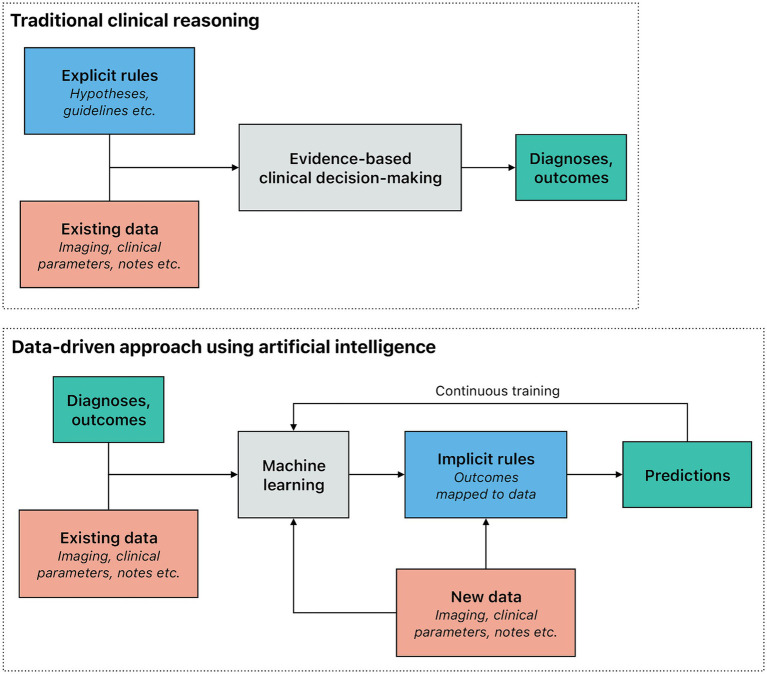
Figure 1.
Traditional reasoning process compared to a data-driven approach using artificial intelligence in a clinical setting. In the traditional reasoning process within a clinical setting, explicit rules (e.g., those derived from pathophysiology) are applied to the observed data (e.g., a patient’s symptoms), to make a diagnosis or predict an outcome. Explicit rules should be based on scientific evidence. The traditional reasoning process is effective in situations where the underlying rules are straightforward and clear. However, it tends to fall short in more complex scenarios. In contrast, machine learning models, which are trained using numerous examples, infer implicit rules by correlating outcomes with the data. This data-driven approach not only adapts better to the presence of multicollinearity but also provides outcomes that are tailored to individual patients, making it particularly valuable for predictive modeling and personalized medicine. Machine learning models can be continuously improved as new data are acquired.