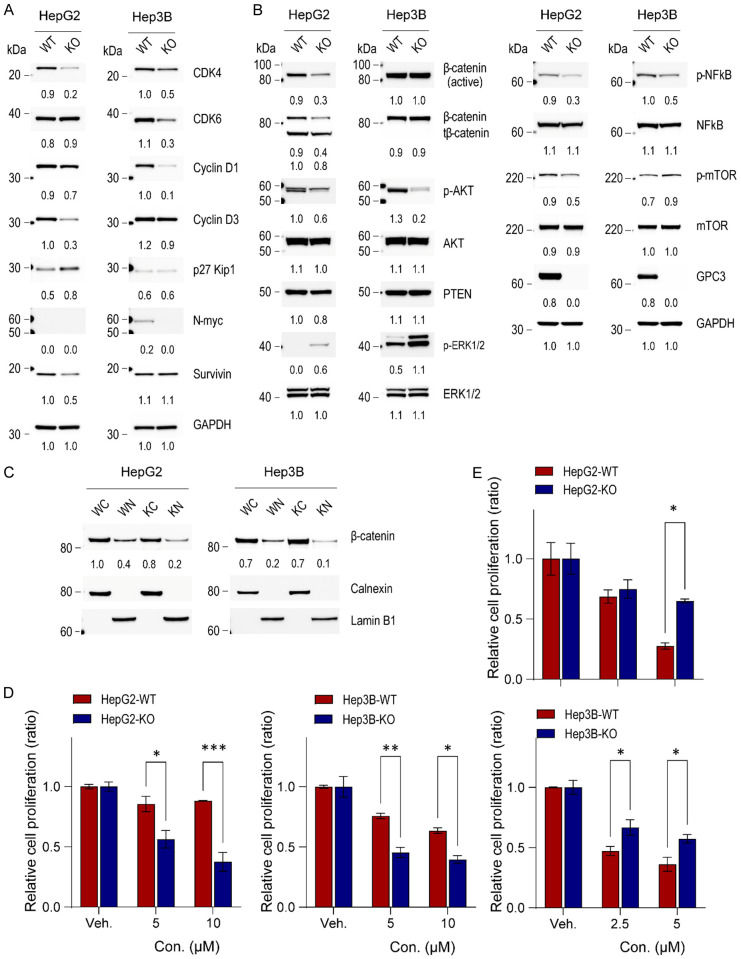
Figure 6.
Impact of GPC3 knockout on cellular signaling in liver cancer cells. (A) Western blot analysis of cell-cycle related molecules, (B) signaling pathways, and (C) cytoplasmic and nuclear protein fractions in HepG2 and Hep3B parental and GPC3 knockout cells. The numerical values beneath the blot images represent the expression levels measured as fold-change. The cytoplasmic proteins were normalized using anti-calnexin antibody, while the nuclear proteins were normalized using anti-lamin B1 as a loading control. WC, wildtype cytoplasmic fraction; WN, wildtype nuclear fraction; KC, GPC3 knockout cytoplasmic fraction; KN, GPC3 knockout nuclear fraction. Additionally, the impacts of ERK and AKT inhibitors on HepG2 and Hep3B parental and GPC3 knockout cells was investigated. Cells were seeded at 2 × 105 cells and then treated with GDC0994 (ERK inhibitor, 5 and 10 µM) (D) or MK2206 (AKT inhibitor, 2.5 and 5 µM) (E) after 24 h. Viable cell numbers were counted on day 2. The data are presented as the mean ± SD. Differences in cell viability were statistically assessed using the t-test. *, P<0.05; **, P<0.01; ***, P<0.001.