Fig. 1.
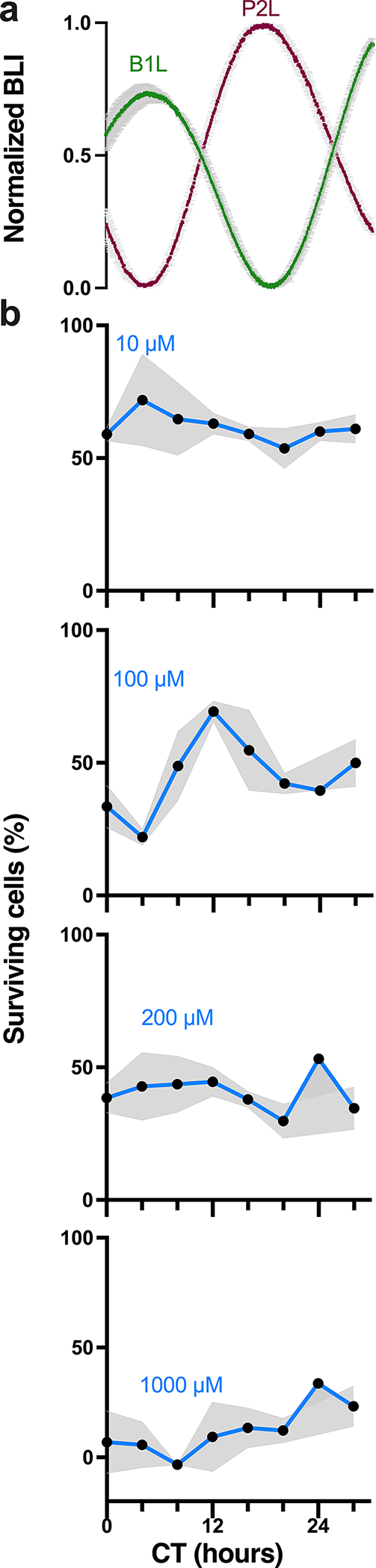
TMZ maximally inhibits growth at the daily peak of Bmal1 expression in GBM cells in vitro. a) Circadian rhythms in clock gene expression recorded as bioluminescence from human LN229 GBM cells transduced with a Per2- or Bmal1-driven luciferase reporter (P2L or B1L, n=2 cultures each, mean ± SEM). b) Survival of LN229-B1L cells varied with the circadian time (CT) and dose of TMZ treatment in vitro. For example, more cells survived 100μM TMZ when administered around the trough of Bmal1 (CT12) than around the peak (CT4). Higher doses of TMZ yielded more cell death and less circadian dependence (n=3 cultures per dose at each time, mean ± SEM, 100μM JTK cycle p = 0.001, ns for 10, 200, 1000μM)
