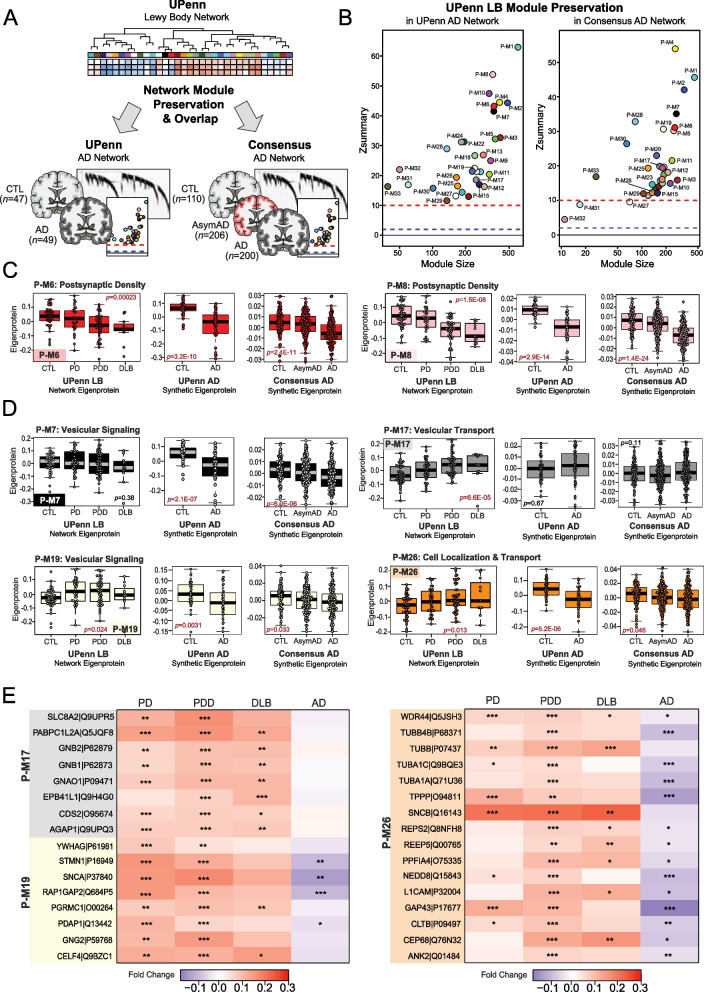
Fig. 5.
Network level proteome comparison between LBD and AD reveals divergent signatures. A Study approach for comparing network-level alterations between the UPenn LBD network and two independent AD networks. The first AD network comprised DLPFC UPenn tissues, including 49 AD cases and the same 47 control cases analyzed in the initial UPenn LBD network. The second AD network was a previously published consensus analysis comprising > 500 control, asymptomatic AD (AsymAD), and AD DLPFC cases from the Banner Sun Health Research Institute and ROSMAP cohorts. Module preservation and overlap analyses were used to compare these networks. B Module preservation analyses of the UPenn LBD network into the UPenn and Consensus AD networks. Modules with a Zsummary score of greater than or equal to 1.96 (q = 0.05, blue dotted line) were considered preserved, while modules with Zsummary scores of greater than or equal to 10 (q = 1.0E-23, red dotted line) were considered highly preserved. C-D UPenn LBD network module eigenproteins associated with the postsynaptic (C) and presynaptic (D) compartments with their corresponding synthetic eigenproteins in the two AD networks. The AD synthetic eigenproteins reflected the weighted module abundance of the top 20% of proteins by kME comprising each LBD module. ANOVA p values are provided for each eigenprotein plot. Box plots represent the median and 25th and 75th percentiles, while data points up to 1.5 times the interquartile range from the box hinge define the extent of error bar whiskers. E Heat maps depicting the fold change magnitude of select presynaptic proteins across UPenn LBD and AD cases. Increases in protein levels are indicated in red, while decreases are in blue. Asterisks in each heat map indicate the statistical significance of the fold change (*, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001). Abbreviations: CTL, control; AsymAD, Asymptomatic Alzheimer’s disease; AD, Alzheimer’s disease; PDD, Parkinson’s disease dementia; DLB, Dementia with Lewy bodies