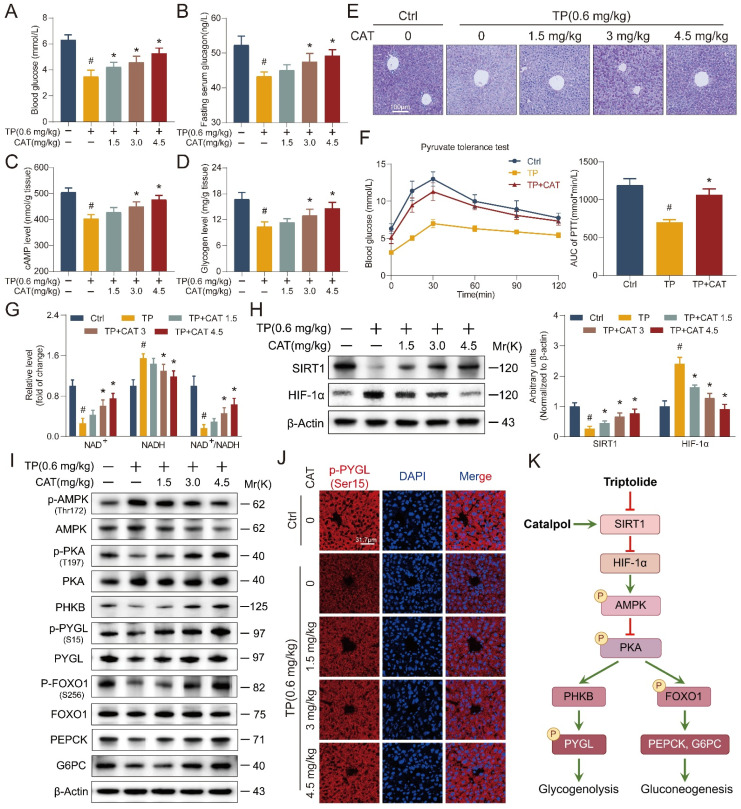
Figure 5.
Catalpol (CAT) alleviated triptolide (TP) induced glycogen metabolism and gluconeogenesis disorders through the SIRT1/HIF-1α pathway. (A) Blood glucose. (B) Fasting serum glucagon levels. (C) Hepatic cAMP levels. (D) Hepatic glycogen levels. (E) Microphotograph of PAS-stained sections of liver tissues. Scale bar, 31.7 μm. (F) Following a 16-hour fasting period, the mice were administered an intraperitoneal injection of sodium pyruvate at a dosage of 1.5 g/kg body weight. Subsequently, their blood glucose levels were recorded at predetermined time intervals. The values for the area under the curve (AUC) of blood glucose were then computed. (G) The relative concentrations of NAD+, NADH and NAD+/NADH ratio measured in liver tissues. (H) Western blot analysis of SIRT1 and HIF-1α expression from mouse liver. (I) The expression levels of glycogenolysis and gluconeogenesis related proteins. (J) Immunofluorescence staining of liver sections using antibody against p-PYGL (Ser15). Scale bar, 31.7 μm. (K) Schematic of signaling pathway changes. Data are expressed as mean ± SD (n = 6); #P < 0.05 versus Ctrl, *P < 0.05 versus TP.