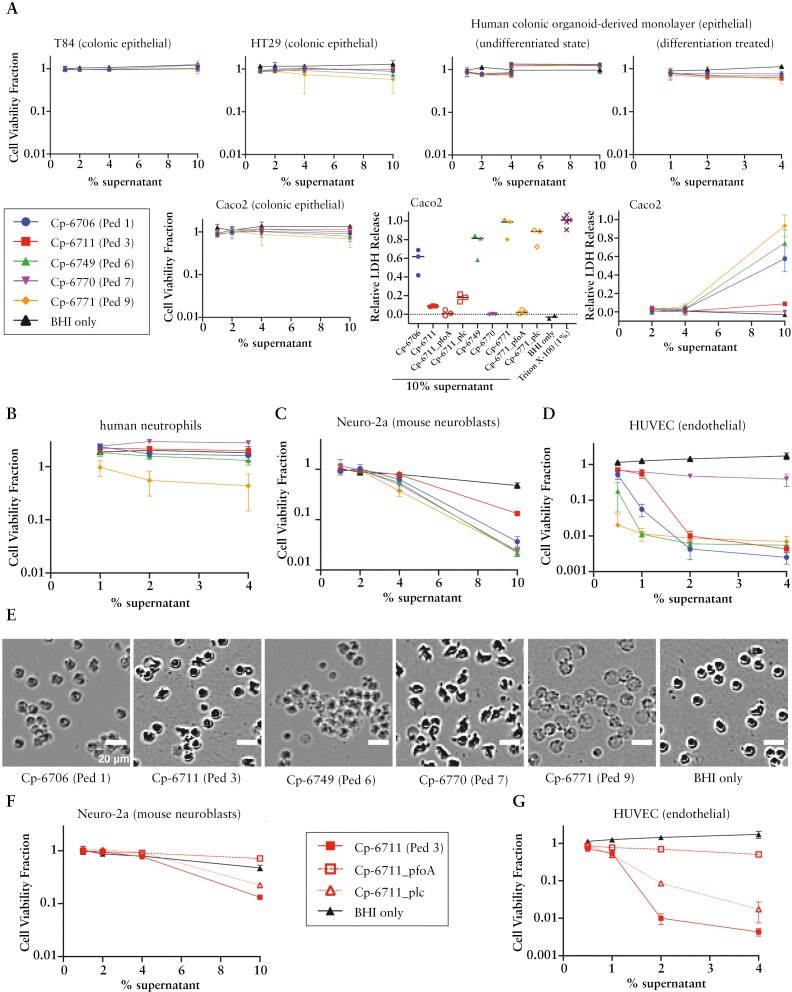
Figure 5.
Toxicity of C. perfringens supernatants on select cell types. C. perfringens isolate supernatants grown in BHI media were incubated with different cells for 20–24 h and measured for viability based on ATP amount [CellTiter-Glo assay]. The cell viability fraction from the CellTiter-Glo assay was calculated by normalizing to the PBS-only control for each cell line. The relative lactate dehydrogenase [LDH] release was normalized to the 100% lysis control [0.5% Triton X-100]. [A] Epithelial cells, [B] isolated human neutrophils, [C] mouse neuroblast cell line Neuro-2a, and [D] human umbilical vein endothelial cells [HUVECs] are shown. Three replicates are shown. [A] Adult colonic organoid-derived monolayer epithelial cells in the undifferentiated state were tested from two adult donors, at 1–4% and 4–10% supernatants. Caco2 cells were additionally incubated with supernatants for 2 h and evaluated for LDH release. [B] Human neutrophils are two replicates each on two patient purifications [four replicates in total]. [E] Representative phase contrast images of human neutrophils with C. perfringens supernatants and BHI media only. Scale bar = 20 µm. [F, G] Bacterial supernatants from C. perfringens toxin mutants grown in BHI were incubated with [F] Neuro-2a and [G] HUVECs for ~24 h and measured for viability by CellTiter-Glo. Three biological replicates are shown.