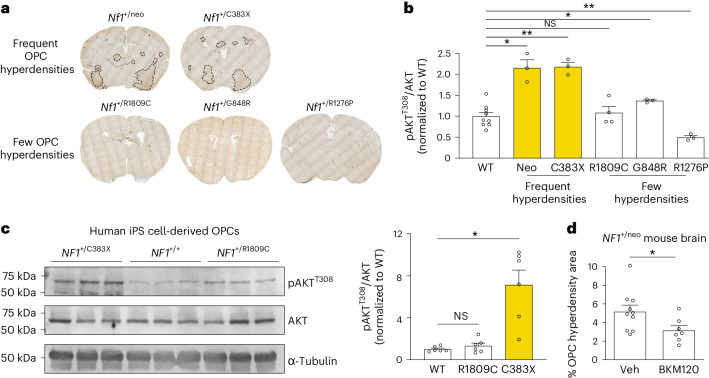
Fig. 4. Heterozygous Nf1-mutant mouse brains contain focal OPC hyperdensities whose formation is Nf1 mutation and PI3K dependent.
a, Focal OPC hyperdensities (labeled by anti-PDGFRα antibody immunohistochemistry, brown) were detected in some, but not all, mice harboring NF1 patient-derived germline Nf1 mutations. b, Immunoblotting revealed >2-fold increased AKT activity (phospho-AKTT308) in the brains of heterozygous Nf1-mutant mice with focal OPC hyperdensities in a relative to WT mice. *P = 0.042 (WT versus neo), 0.0138 (WT versus G848R); **P = 0.0015 (WT versus C383X), 0.0022 (WT versus R1276P). N = 9, 3, 3, 4, 3 and 3 (left to right). c, Immunoblotting of human iPS cell-derived OPCs heterozygous for NF1+/C383X, but not NF1+/R1809C, mutations have increased AKT activity (phospho-AKTT308) relative to WT OPCs. *P = 0.0135. N = 6 per group. d, Immunohistochemistry for the OPC marker PDGFRα revealed reduced area of focal OPC hyperdensities in the brains of Nf1+/neo mice treated with NVP-BKM120 relative to mice treated with vehicle control (Veh). Unpaired t-test with Welch’s correction. N = 10,7 (left to right). *P = 0.0316. Brown–Forsythe ANOVA test with Dunnett’s T3 multiple comparisons (b, F = 29.16; c, F = 17.52). Data shown as mean ± s.e.m.; each point represents one mouse (b–d); two-sided; NS, not significant (P > 0.05).