Figure 3.
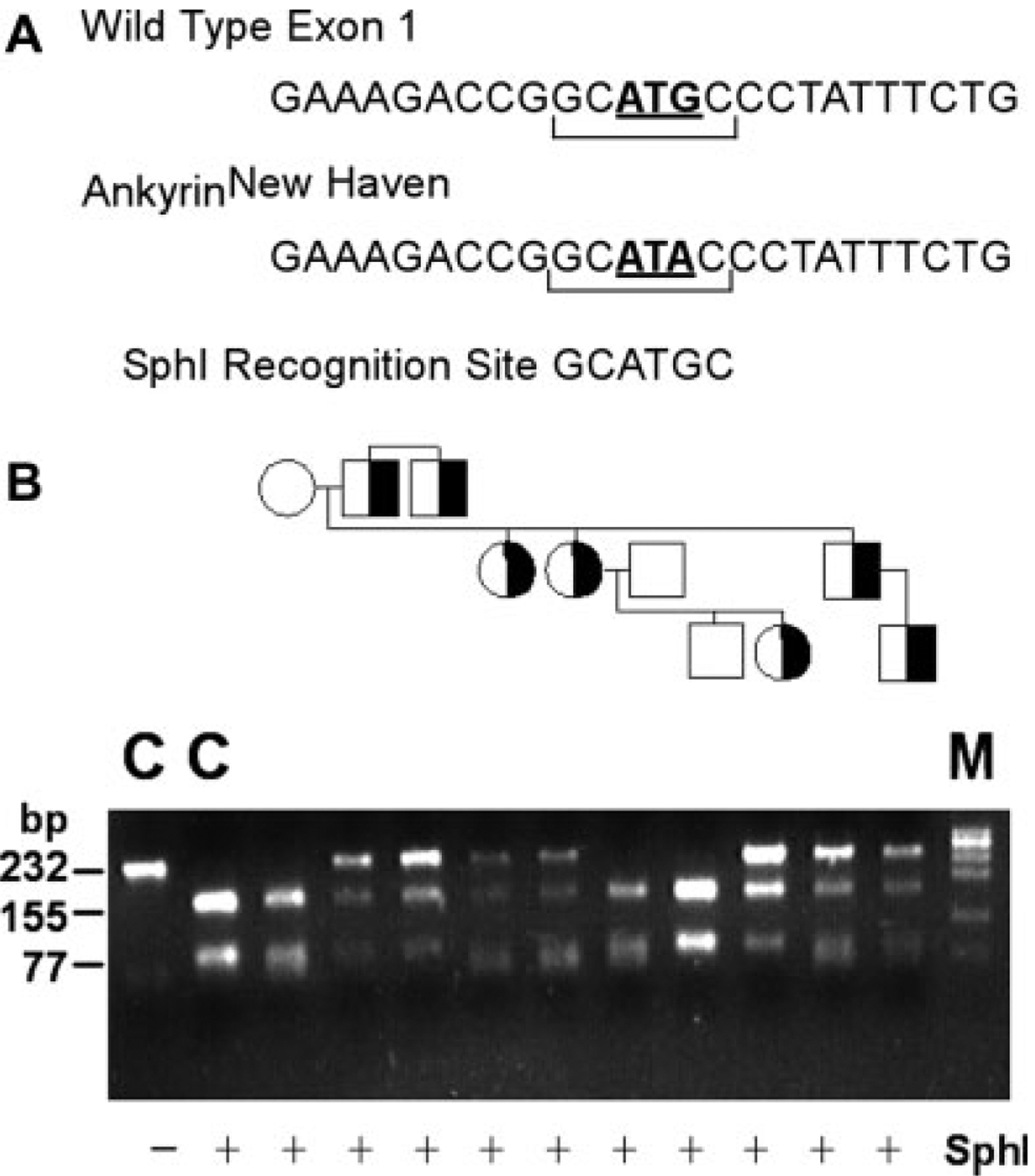
Analysis of the ankyrinNew Haven mutation in a three generation, African–American kindred. A: The ankyrinNew Haven mutation abolishes a SphI restriction site, allowing discrimination of wild-type and mutant alleles. B: The region of the ankyrin gene containing the ankyrinNew Haven mutation was amplified by PCR from genomic DNA of the proband, his family members, and a normal control (C), amplification products digested with SphI, fractionated by agarose gel electrophoresis, and visualized by ethidium bromide staining. The control PCR product yields a 232 bp fragment (Lane 1) which after SphI digestion cleaves into fragments of 155 and 77 bp (Lane 2). Amplification products from unaffected patients demonstrate patterns of SphI digestion similar to control. Digestion of amplification products from spherocytosis patients yields fragments of 155 and 77 bp, as well as an undigested fragment of 232 bp, indicating heterozygosity for the ankyrinNew Haven allele. Half-filled symbols indicate hereditary spherocytosis individuals. M indicates marker.
