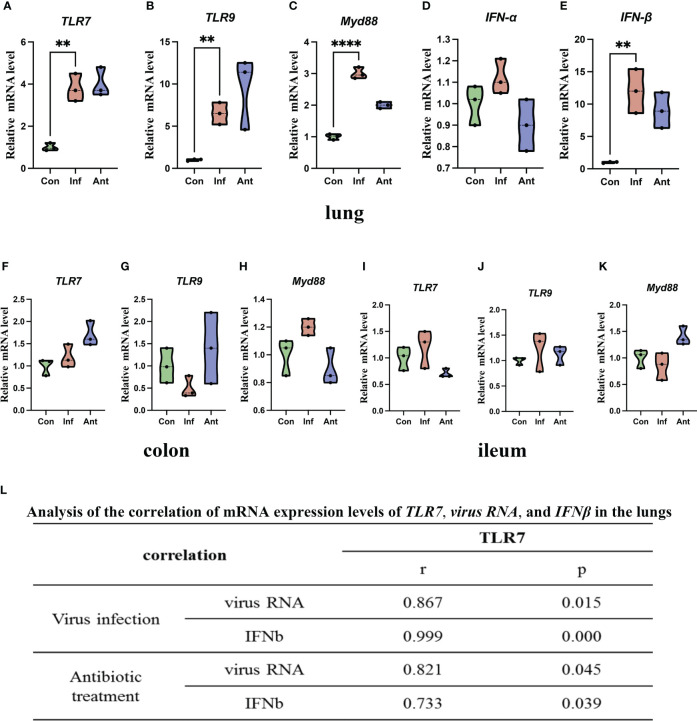
Figure 2.
Increased viral RNA, TLR7 signaling, and IFN-α and IFN-β mRNA expression in the lungs, colon, ileum, and their correlation. (A) TLR7 mRNA level; (B) TLR9 mRNA level; (C) Myd88 mRNA level; (D) IFN-α mRNA level; (E) IFN-β mRNA level in the lungs and (F) TLR7 mRNA level; (G) TLR9 mRNA level; (H) Myd88 mRNA level in the colon; (I) TLR7 mRNA level; (J) TLR9 mRNA level; (K) Myd88 mRNA level in the ileum. (L) Expression of TLR7 correlated with viral RNA and IFN-β mRNA levels in the lungs of the virus- and antibiotic-treated mice. Each dot represents data from one animal. Data are mean ± SEM. n = 3. Con: Female BALB/c mice aged 6 to 7 weeks (20 ± 2 g) were treated with PBS; Inf group: Female BALB/c mice aged 6 to 7 weeks (20 ± 2 g) were treated with influenza virus infection; Ant group: Female BALB/c mice aged 6 to 7 weeks (20 ± 2 g) were treated with combination of antibiotics. Statistical analysis was performed by independent samples T test. **P < 0.01; ****P < 0.0001. All replicates are biological.