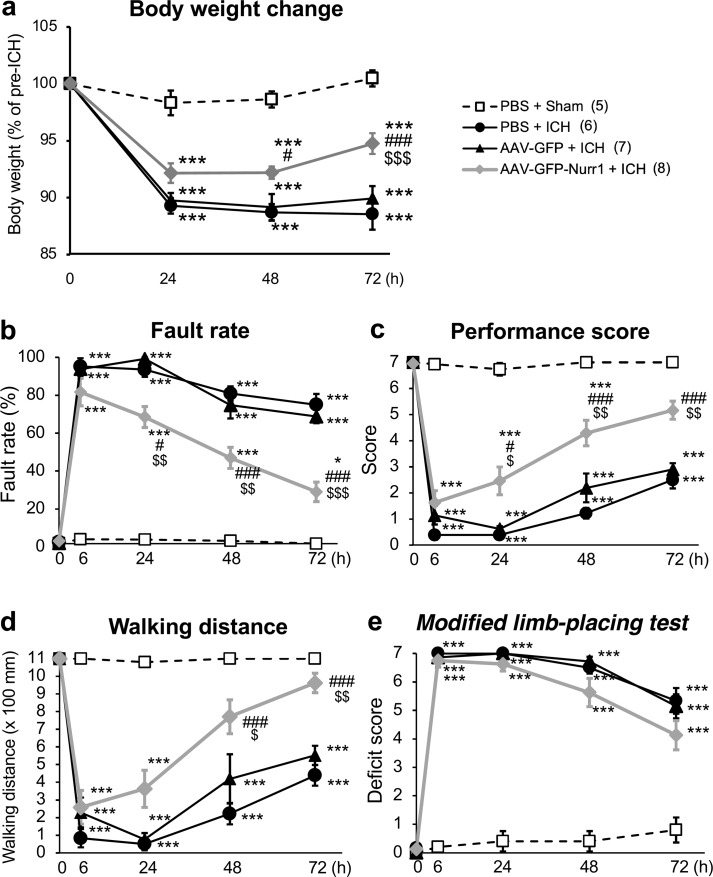
Fig. 2.
Effect of Nurr1 overexpression on body weight change and motor dysfunction after ICH induction. a Time-dependent changes in body weight of mice after sham operation or ICH induction. Significant differences between groups were observed by two-way repeated measure ANOVA (interactions, F9, 66 = 11.63, P < 0.001; time, F3, 66 = 121.9, P < 0.001; treatment, F3, 22 = 25.84, P < 0.001). b-d Results in the beam-walking test were evaluated by fault rate (b), performance score (c) and walking distance (d). Significant differences between groups were observed by two-way repeated measure ANOVA concerning the fault rate (interactions, F12, 88 = 19.21, P < 0.001; time, F4, 88 = 167.4, P < 0.001; treatment, F3, 22 = 90.38, P < 0.001), the performance score (interactions, F12, 88 = 14.10, P < 0.001; time, F4, 88 = 125.8, P < 0.001; treatment, F3, 22 = 90.47, P < 0.001) and the walking distance (interactions, F12, 88 = 8.146, P < 0.001; time, F4, 88 = 64.23, P < 0.001; treatment, F3, 22 = 56.00, P < 0.001). e Results in the modified limb-placing test. Significant differences between two groups were observed by two-way repeated measure ANOVA (interactions, F12, 88 = 17.82, P < 0.001; time, F4, 88 = 203.1, P < 0.001; treatment, F3, 22 = 145.7, P < 0.001). ∗P < 0.05 and ∗∗∗P < 0.001 versus PBS + sham; #P < 0.05 and ###P < 0.001 versus PBS + ICH; $ P < 0.05, $$ P < 0.01 and $$$ P < 0.001 versus AAV-GFP + ICH. Post hoc test was based on Sidak's multiple comparison test (a) or Bonferroni's method (b-e). Number of mice examined was 5 in PBS + sham group, 6 in PBS + ICH group, 7 in AAV-GFP + ICH group and 8 in AAV-GFP-Nurr1 + ICH group, respectively.