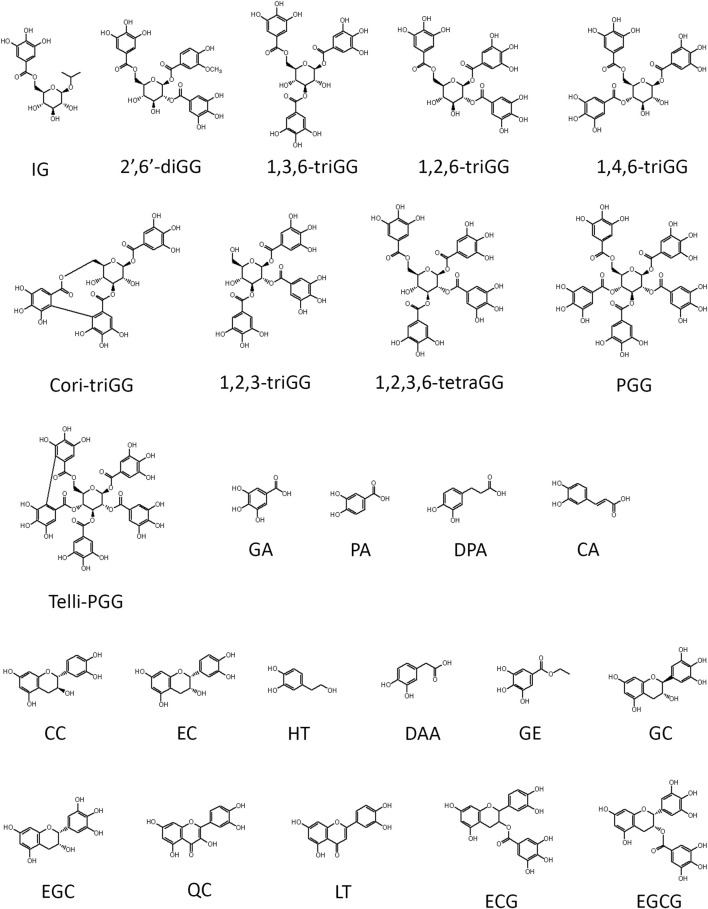
FIGURE 1.
Structure summary of polyphenols utilized in this study. Ten gallotannins used in this study include 2-isopropyl-O‐β‐(6′‐O‐galloyl)‐glucopyranoside (IG), 4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenol 1-O-β-D-(2′,6′-di-O-galloyl) glucoside (2′,6′-diGG), 1,3,6-tri-O-galloyl-β-D-glucose (1,3,6-triGG), 1,2,6-tri-O-galloyl-β-D-glucose (1,2,6-triGG), 1,4,6-tri-O-galloyl-β-D-glucose (1,4,6-triGG), corilagin (Cori-triGG), 1,2,3-tri-O-galloyl-beta-D-glucose (1,2,3-triGG), 1,2,3,6-tetragalloyl-beta-D-glucose (1,2,3,6-tetraGG), 1,2,3,4,6-penta-O-galloyl-β-D-glucose (PGG), tellimagrandin II (Telli-PGG). Fifteen dietary polyphenol used in this study consist of gallic acid (GA), protocatechuic acid (PA), 3,4-dihydroxyphenylpropionic acid (DPA), caffeic acid (CA), (+)‐catechin (CC), (−)‐epicatechin (EC), hydroxytyrosol (HT), 3,4-dihydroxyphenylacetic acid (DAA), gallic acid ethyl ester (GE), (−)‐gallocatechin (GC), (−)‐epigallocatechin (EGC), quercetin (QC), luteolin (LT), (−)-epicatechin-3-gallate (ECG), and epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG).