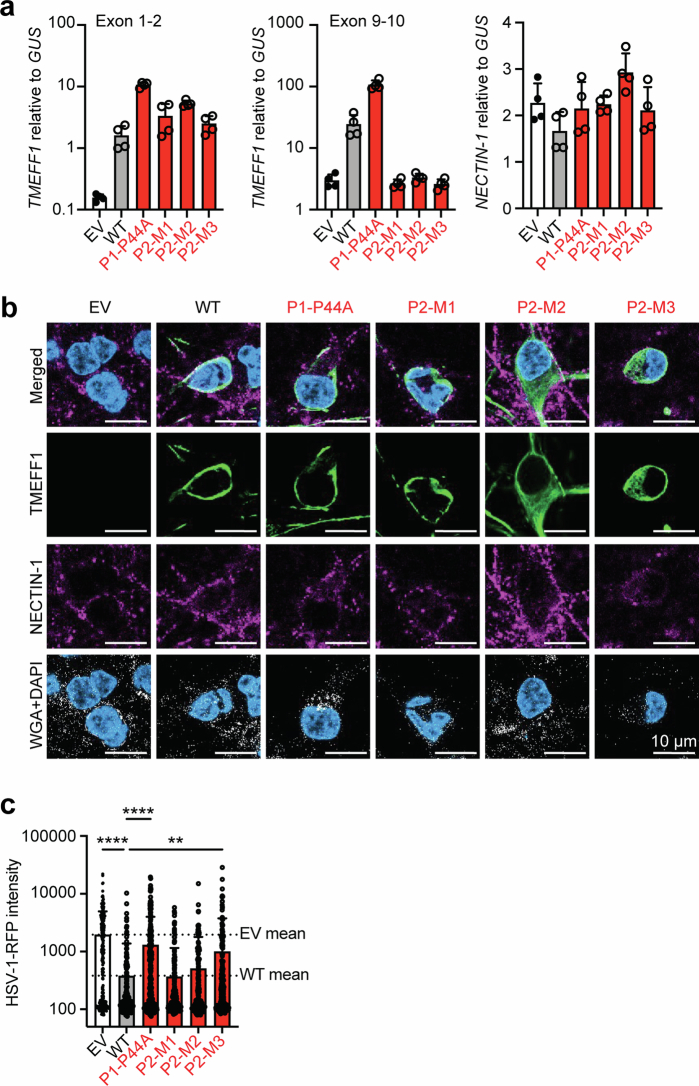
Extended Data Fig. 11. Exogenous expression of wild-type but not mutant TMEFF1 renders TMEFF1 KO neurons normally resistant to HSV-1 infection.
a, TMEFF1 and NECTIN1 mRNA levels, as measured by RT-qPCR, in TMEFF1 KO cortical neurons transduced with an EV, WT TMEFF1 or patient-specific mutant TMEFF1-expressing lentivirus. Two probes, targeting exons 1-2 (left) and exons 9-10 (center) of TMEFF1, were used. The data shown are representative of two independent experiments. b, Immunostaining of exogenous TMEFF1 (green), endogenous NECTIN-1 (purple), AT-rich DNA (DAPI, blue) and the cell membrane (WGA, white), for hPSC-derived TMEFF1 KO cortical neurons transduced with EV, WT TMEFF1 or patient-specific mutant TMEFF1-expressing lentiviruses. The data shown are representative of three independent experiments. c, Measurement of RFP intensity, 10 h after infection with HSV-1-RFP, in TMEFF1 KO cortical neurons transduced with EV, WT TMEFF1 or patient-specific mutant TMEFF1-expressing lentiviruses. Cortical neurons were labeled with anti-TMEFF1 antibody (green) and DAPI (blue). RFP intensity was assessed under a confocal microscope. HSV-1 infection results in the expression of RFP, which is detected in the nucleus at 10 hpi. Statistical analysis was conducted with Kruskal-Wallis tests with Dunn’s test for multiple comparisons. **p-value < 0.01; ****p-value < 0.0001. The data are presented as the mean ± SEM from three independent experiments.