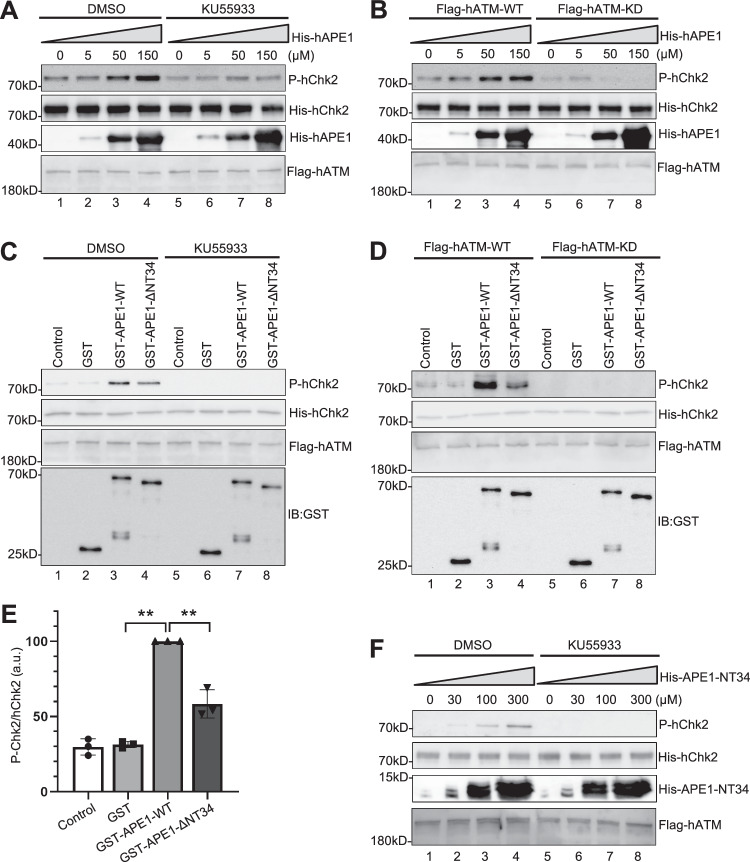
Fig. 4. APE1 directly stimulates ATM kinase activity in vitro.
A In vitro kinase assays were performed with different concentrations of His-tagged human APE1 (His-hAPE1) as indicated, Flag-tagged WT human ATM (Flag-hATM) and His-tagged kinase-deficient human Chk2 (His-hChk2), with DMSO or ATM inhibitor KU55933 (1 mM). ATM kinase activity was indicated by Chk2 phosphorylation (P-hChk2) via immunoblotting using anti-Chk2 T68 phosphorylation specific antibodies. B Kinase assays were performed with different concentrations of His-hAPE1 as indicated, WT or KD (kinase-dead) Flag-hATM and His-hChk2. ATM kinase activity was indicated by P-hChk2. C Kinase assays were performed with Control (PBS), GST, WT or ΔNT34 GST-Xenopus APE1, Flag-hATM and His-hChk2, with the addition of DMSO or KU55933 (1 mM). ATM kinase activity was indicated by P-hChk2. D Kinase assays were performed with Control (PBS), GST, GST-Xenopus APE1 WT or ΔNT34, Flag-tagged WT or kinase-dead (KD) ATM and His-hChk2. ATM kinase activity was indicated by P-hChk2. E Quantification and statistical analysis of the ratio of P-hChk2 vs. hChk2 from Panel C. Data are presented as mean values ± SD. **p(GST vs GST-APE1-WT) = 0.0001; **p(GST-APE1-WT vs GST-APE1-ΔNT34) = 0.0016; two-tailed, unpaired t-test, n = 3. F Kinase assays were performed with different concentrations of His-tagged APE1 NT34 (His-APE1-NT34) and DMSO/KU55933 as indicated. Chk2 phosphorylation was examined via immunoblotting analysis. The data presented in Panel A–D and F are representative of three biological replicates. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.