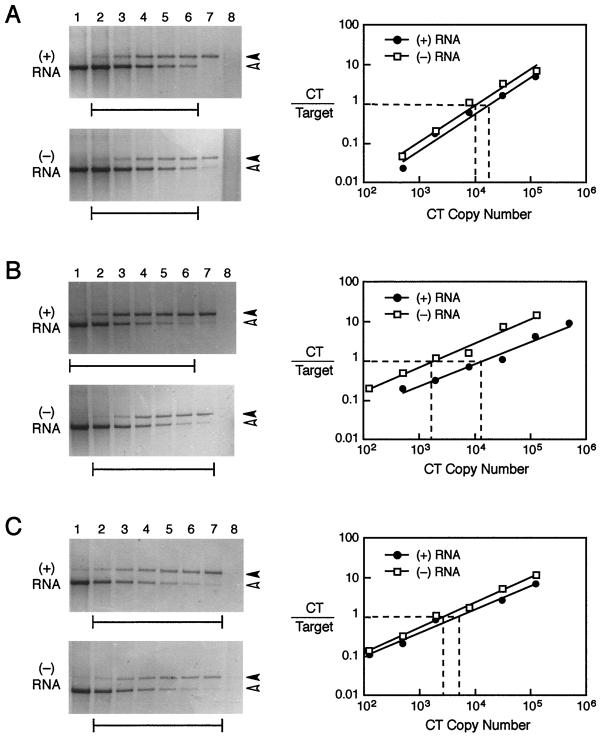
FIG. 2.
Quantitation of plus (+)- and minus (−)-strand viral RNAs during acute and persistent infection. Competitive, strand-specific RT-PCR was used to measure the levels of plus and minus strands of viral RNA. The solid arrowhead marks the position of the target amplicon, and the open arrowhead marks the competitive template. Brackets underneath each gel indicate which lanes were used for quantitation, as shown in the adjacent plot. Representative data are shown, and a summary of data from all experiments is presented in Table 2. (A) Control plus and minus transcripts were input at 4 × 104 copies per reaction and used to evaluate the efficiency of the strand-specific competitive RT-PCR procedure. (B) Acutely infected muscle at 7 days postinfection showed a 61-fold excess of plus strand with 1.3 × 104 copies per 0.5 μg of input RNA for the plus strand and 1.7 × 103 copies per 4 μg of input RNA for the minus strand. (C) At 1 month after infection, the plus strand was present at 5.1 × 103 copies per 4 μg of input RNA while the minus strand was at 2.6 × 103 copies per 4 μg, yielding a final plus-strand-to-minus-strand ratio of 2.0.