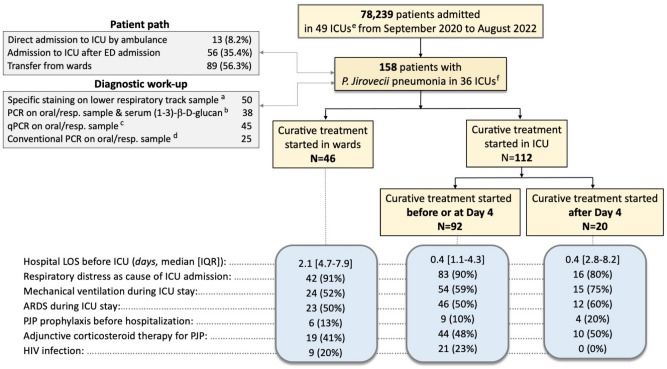
Fig. 1.
Flow chart. ARDS acute respiratory distress syndrome, ICU intensive care unit, IQR interquartile range, LOS length of stay, PCR polymerase chain reaction (either conventional i.e., not quantitative or quantitative), PJP Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia, qPCR quantitative PCR. ARDS was defined according to the Berlin definition [47]. aDiagnostic of PJP made by the pathologist using microscopy and specific staining (modified Toluidine Blue O, Grocott-Gomori methenamine silver, or Immunofluorescent-antibody staining). bIn every case, the diagnosis of PJP was based on a positive quantitative or non-quantitative PCR test performed on oral wash (%) or on lower respiratory tract sample, and serum (1–3)-b-d-glucan positivity (threshold for positivity left to the appreciation of the attending intensivist) [48], but also on the presence of bilateral interstitial pneumonia and a diagnostic workup that ruled out other diagnoses. cIn every case, the diagnosis of PJP was based on a positive quantitative PCR test with sufficiently low cycle threshold (Ct) (left to the appreciation of the attending intensivist), but also on the presence of bilateral interstitial pneumonia and a diagnostic workup that ruled out other diagnoses. dIn every case, the diagnosis of PJP was based on a positive non-quantitative PCR test performed on oral wash (%) or on lower respiratory tract sample, but also on the presence of either bilateral interstitial infiltrates on chest X-ray or bilateral ground glass opacities on high-resolution lung computed tomography and a diagnostic workup that ruled out other diagnoses. eAmong the 36 participating ICUs, 18 were in university affiliated hospitals. f13 ICUs, including 6 ICUs in university affiliated hospitals, did not admit any patient with PJP during the study period