Figure.
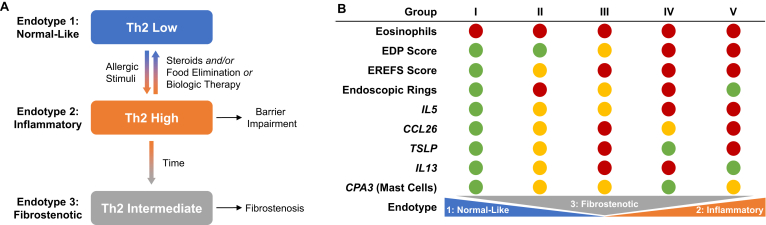
Endotypes of eosinophilic esophagitis and their characteristic features. (A) Model depicting patient progression from Th2-low phenotype (endotype 1) to a Th2-high phenotype (endotype 2) following allergic or inflammatory insult. On steroid treatment, food elimination, or biologic therapy the Th2-gene expression decreases and patients either resolve inflammation by reverting to a Th2-low phenotype or develop a fibrostenotic (endotype 3) signature. (B) Five subgroups of patients with active EoE were identified based on a variety of criteria, including expression of IL5, IL13, CCL26, TSLP, and CPA3. Relative levels of each criterion are reported in red (high), yellow (intermediate), or green (low). The 5 groups differed in the EoE endotypes spanned, but not in eosinophil levels, which were universally high. Group V patients had the highest expression of IL5, TSLP, CCL26, and genes associated with tissue remodeling. Groups II and III (which exhibited intermediate expression of IL5 and CPA3) were differentiated by high TSLP and IL13 in group III. CCL26, C-C motif chemokine ligand 26; EDP, eosinophilic esophagitis diagnostic panel; EREFS, endoscopic reference score; Th2, T helper cell type 2; TSLP, thymic stromal lymphopoietin (Adapted from J Allergy Clin Immunol: 2020;145:1629–1640.e4.).31