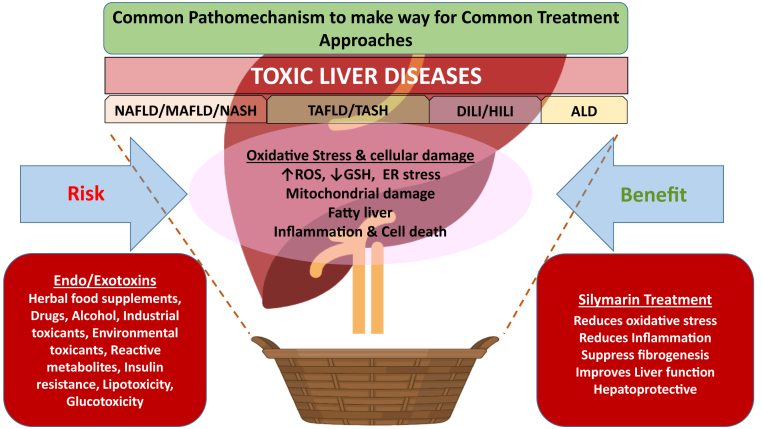
Figure.
Common oxidative stress mechanism underlies hepatocellular damage by several exogenous and endogenous toxins. Merging clinical phenotypes of fatty liver disease (NAFLD/MAFLD, NASH, DILI, ALD) into a single basket entity, toxic liver diseases (TLDs), based on common pathomechanism will allow clinicians to evaluate the benefits of silymarin as an antioxidant and potential hepatoprotective agent.