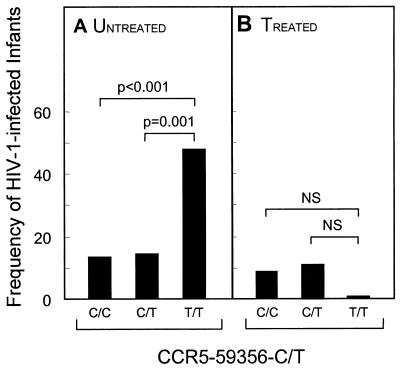
FIG. 3.
(A) Untreated African-American CCR5-59356-T mutant homozygotes have a highly significantly (P < 0.001) increased rate of HIV-1 transmission (47.6% of 21 individuals) compared to CCR5-59356-C wild-type homozygotes (13.4% of 187) or heterozygotes (14% of 71). (B) The enhancing effect of the CCR5-59356-T mutation on HIV-1 transmission was not observed in the AZT-treated group. NS, not significant.