Abstract
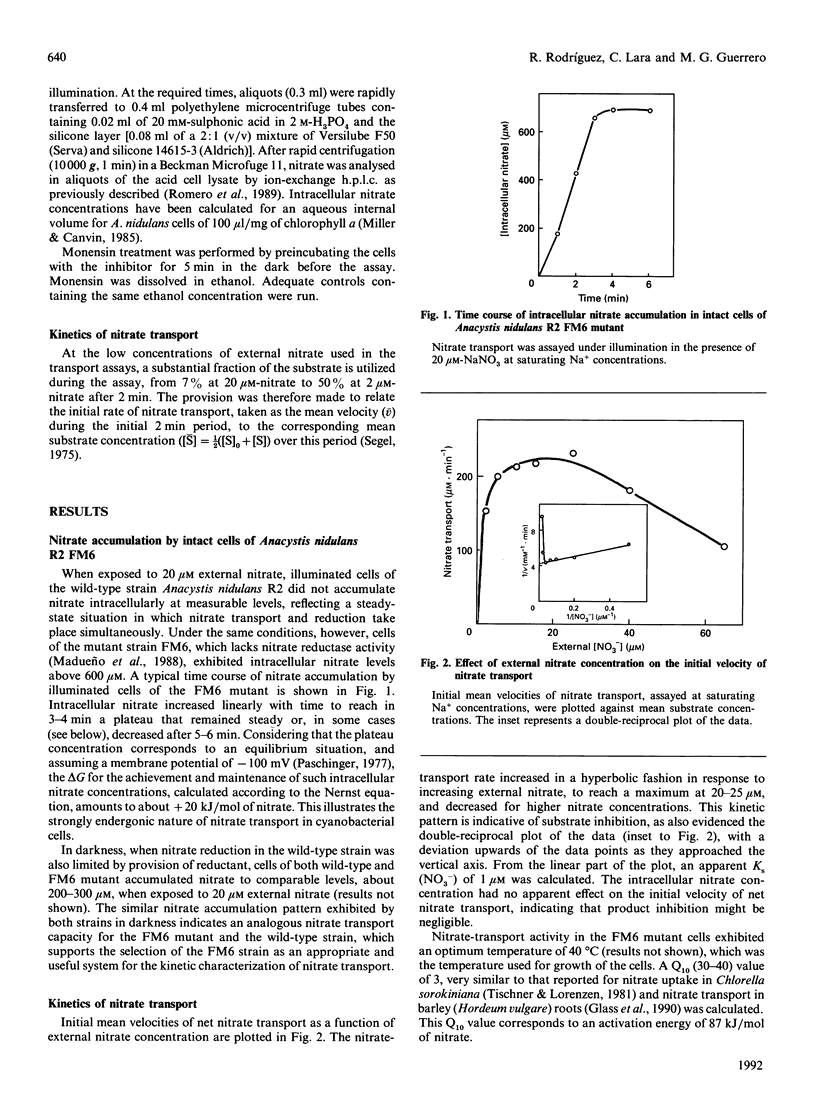
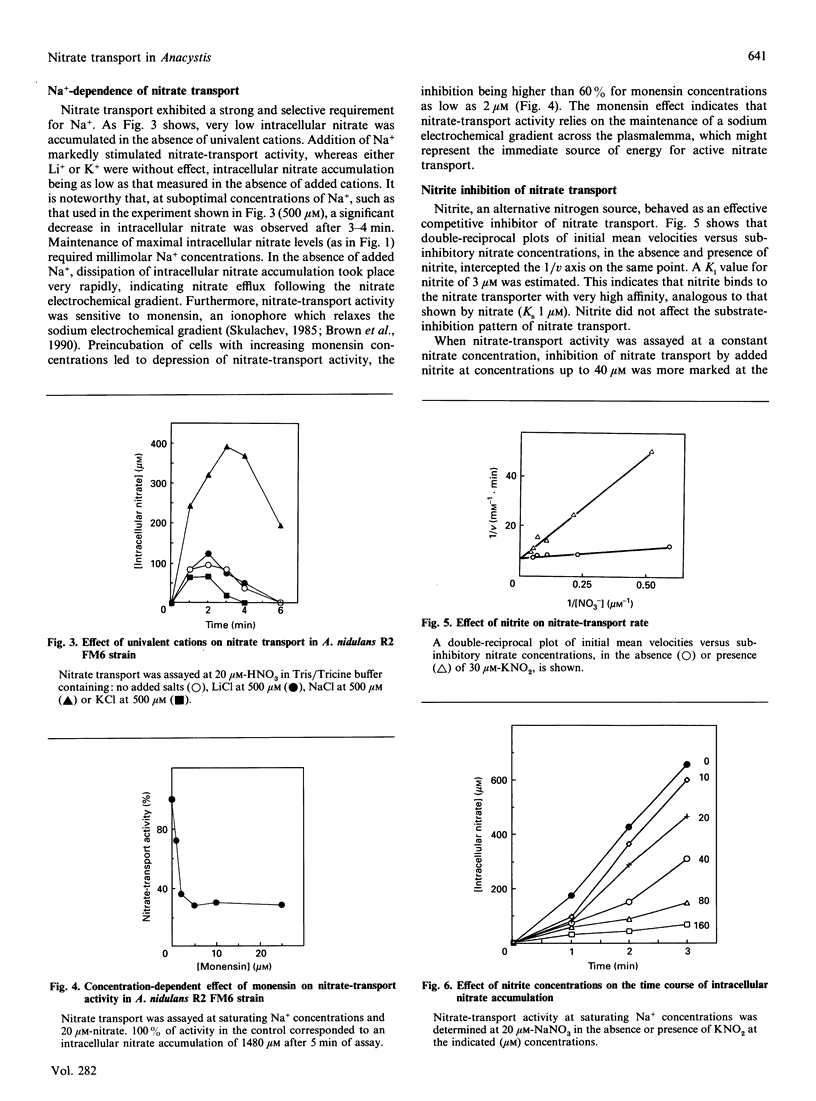
Nitrate transport has been studied in the cyanobacterium Anacystis nidulans R2 by monitoring intracellular nitrate accumulation in intact cells of the mutant strain FM6, which lacks nitrate reductase activity and is therefore unable to reduce the transported nitrate. Kinetic analysis of nitrate transport as a function of external nitrate concentration revealed apparent substrate inhibition, with a peak velocity at 20-25 microM-nitrate. A Ks (NO3-) of 1 microM was calculated. Nitrate transport exhibited a stringent requirement for Na+. Neither Li+ nor K+ could substitute for Na+. Monensin depressed nitrate transport in a concentration-dependent manner, inhibition being more than 60% at 2 microM, indicating that the Na(+)-dependence of active nitrate transport relies on the maintenance of a Na+ electrochemical gradient. The operation of an Na+/NO3- symport system is suggested. Nitrite behaved as an effective competitive inhibitor of nitrate transport, with a Ki (NO2-) of 3 microM. The time course of nitrite inhibition of nitrate transport was consistent with competitive inhibition by mixed alternative substrates. Nitrate and nitrite might be transported by the same carrier.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blumwald E., Wolosin J. M., Packer L. Na+/H+ exchange in the cyanobacterium Synechococcus 6311. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Jul 18;122(1):452–459. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)90497-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown I. I., Fadeyev S. I., Kirik I. I., Severina I. I., Skulachev V. P. Light-dependent delta mu Na-generation and utilization in the marine cyanobacterium Oscillatoria brevis. FEBS Lett. 1990 Sep 17;270(1-2):203–206. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)81268-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleland W. W. Substrate inhibition. Methods Enzymol. 1979;63:500–513. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Espie G. S., Miller A. G., Canvin D. T. Characterization of the na-requirement in cyanobacterial photosynthesis. Plant Physiol. 1988 Nov;88(3):757–763. doi: 10.1104/pp.88.3.757. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glass A. D., Siddiqi M. Y., Ruth T. J., Rufty T. W. Studies of the Uptake of Nitrate in Barley : II. Energetics. Plant Physiol. 1990 Aug;93(4):1585–1589. doi: 10.1104/pp.93.4.1585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lara C., Romero J. M., Guerrero M. G. Regulated nitrate transport in the cyanobacterium Anacystis nidulans. J Bacteriol. 1987 Sep;169(9):4376–4378. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.9.4376-4378.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- London W. P., Steck T. L. Kinetics of enzyme reactions with interaction between a substrate and a (metal) modifier. Biochemistry. 1969 Apr;8(4):1767–1779. doi: 10.1021/bi00832a061. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller A. G., Turpin D. H., Canvin D. T. Na+ requirement for growth, photosynthesis, and pH regulation in the alkalotolerant cyanobacterium Synechococcus leopoliensis. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jul;159(1):100–106. doi: 10.1128/jb.159.1.100-106.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison J. F. Approaches to kinetic studies on metal-activated enzymes. Methods Enzymol. 1979;63:257–294. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)63013-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paschinger H. DCCD induced sodium uptake by Anacystis nidulans. Arch Microbiol. 1977 Jun 20;113(3):285–291. doi: 10.1007/BF00492037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romero J. M., Lara C., Guerrero M. G. Determination of intracellular nitrate. Biochem J. 1989 Apr 15;259(2):545–548. doi: 10.1042/bj2590545. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sivak M. N., Lara C., Romero J. M., Rodríguez R., Guerrero M. G. Relationship between a 47-kDa cytoplasmic membrane polypeptide and nitrate transport in Anacystis nidulans. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Jan 16;158(1):257–262. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(89)80206-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skulachev V. P. Membrane-linked energy transductions. Bioenergetic functions of sodium: H+ is not unique as a coupling ion. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Sep 2;151(2):199–208. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb09088.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


