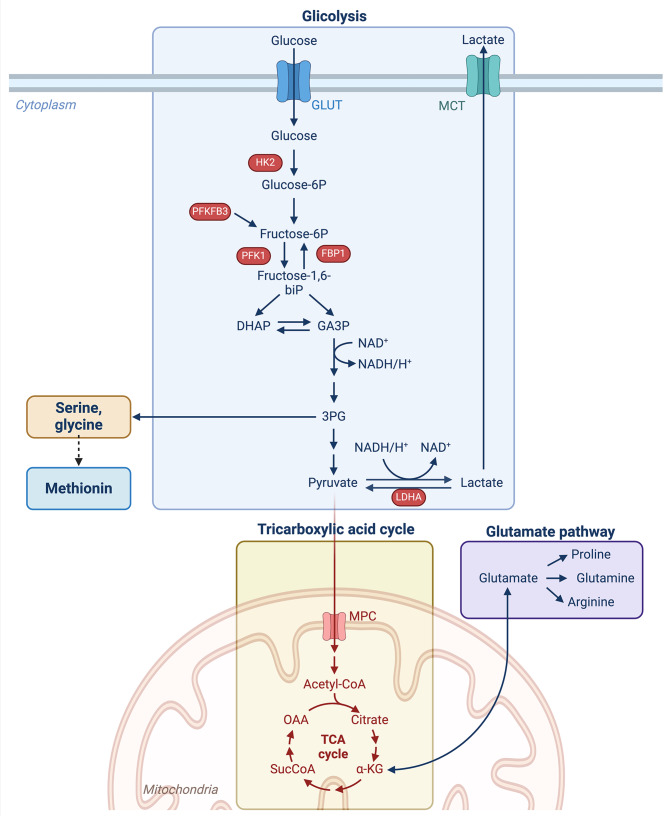
Fig. 1.
Interconnection between glycolysis, TCA cycle, and amino acids metabolism. During glycolysis, glucose is broken down to two molecules of pyruvate. One of the glycolysis intermediate, 3PG, can be converted to serine, glycine and indirectly to methionine (See Fig. 5 for details). Pyruvate is translocated to mitochondria for the oxidative decarboxylation into acetyl-CoA. Acetyl-CoA is oxidated via the TCA cycle and sustains the production of ATP from ADP in the oxidative phosphorylation process. α-KG produced during the TCA cycle, can be converted to glutamate and vice-versa. Glutamate is the starting point for the production of proline, glutamine and arginine. Abbreviations: GLUT = glucose transporter; MCT = monocarboxylate transporter; HK2 = hexokinase 2; PFKFB3 = 6-phosphofructo-2-kinase/fructose-2,6-biphosphatase 3; PFK1 = 6-phosphofructokinase; FBP1 = fructose-bisphosphatase 1; fructose-1,6-biP = fructose-1,6-biphosphate; DHAP = dihydroxyacetone phosphate; GA3P = glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate; TCA= tricarboxylic acid cycle; 3PG = 3-phosphoglycerate; LDHA = lactate dehydrogenase A; α-KG = α-ketoglutarate; Acetyl-CoA = acetyl coenzyme A