Abstract
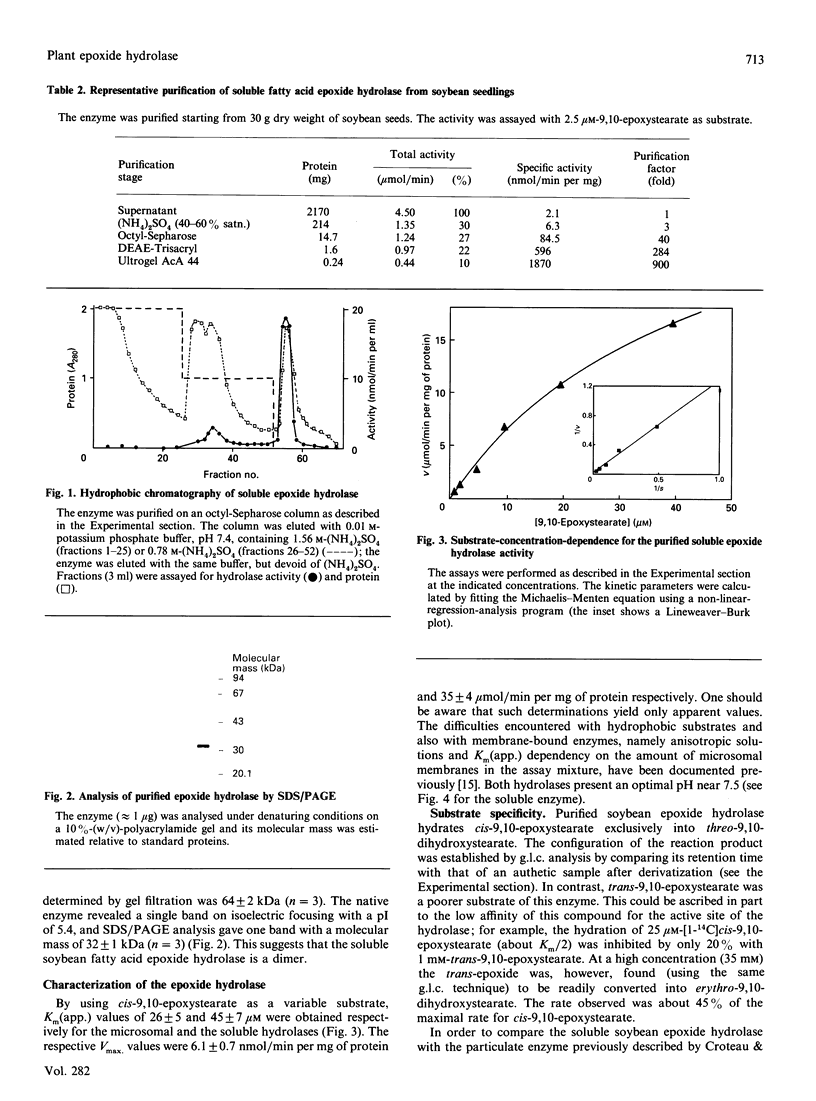
Epoxide hydrolases catalysing the hydration of cis-9,10-epoxystearate into threo-9,10-dihydroxystearate have been detected in soybean (Glycine max) seedlings. The major activity was found in the cytosol, a minor fraction being strongly associated with microsomes. The soluble enzyme, which was purified to apparent homogeneity by (NH4)2SO4 fractionation, hydrophobic, DEAE- and gel-filtration chromatographies, has a molecular mass of 64 kDa and a pI of 5.4.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blée E., Schuber F. Efficient epoxidation of unsaturated fatty acids by a hydroperoxide-dependent oxygenase. J Biol Chem. 1990 Aug 5;265(22):12887–12894. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Croteau R., Kolattukudy P. E. Biosynthesis of hydroxyfatty acid polymers. Enzymatic epoxidation of 18-hydroxyoleic acid to 18-hydroxy-cis-9,10-epoxystearic acid by a particulate preparation from spinach (Spinacia oleracea). Arch Biochem Biophys. 1975 Sep;170(1):61–72. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(75)90097-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill S. S., Hammock B. D. Hydration of cis- and trans-epoxymethyl stearates by the cytosolic epoxide hydrase of mouse liver. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Aug 13;89(3):965–971. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)91872-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guenthner T. M., Oesch F. Identification and characterization of a new epoxide hydrolase from mouse liver microsomes. J Biol Chem. 1983 Dec 25;258(24):15054–15061. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu A. Y., Jerina D. M., Levin W. Liver microsomal epoxide hydrase. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jun 10;252(11):3715–3723. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meijer J., DePierre J. W. Cytosolic epoxide hydrolase. Chem Biol Interact. 1988;64(3):207–249. doi: 10.1016/0009-2797(88)90100-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrissey J. H. Silver stain for proteins in polyacrylamide gels: a modified procedure with enhanced uniform sensitivity. Anal Biochem. 1981 Nov 1;117(2):307–310. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90783-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orsi B. A., Tipton K. F. Kinetic analysis of progress curves. Methods Enzymol. 1979;63:159–183. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)63010-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watabe T., Komatsu T., Isobe M., Tsubaki A. Mouse liver microsomal cholesterol epoxide hydrolase: a specific inhibition of its activity by 5,6 alpha-Imino-5 alpha-cholestan-3 alpha-OL. Chem Biol Interact. 1983 Apr-May;44(1-2):143–154. doi: 10.1016/0009-2797(83)90136-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



