Abstract
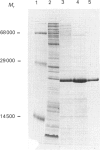
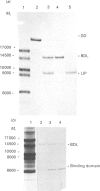
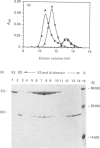
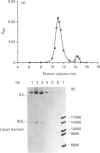
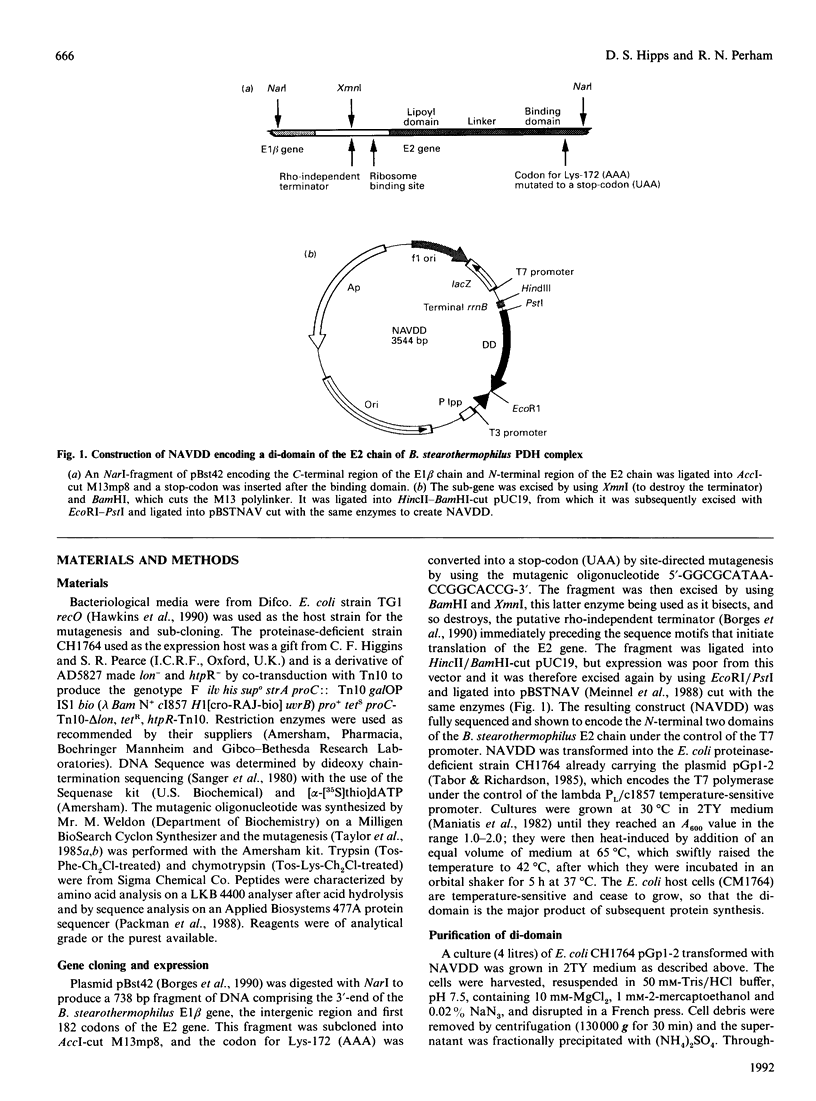
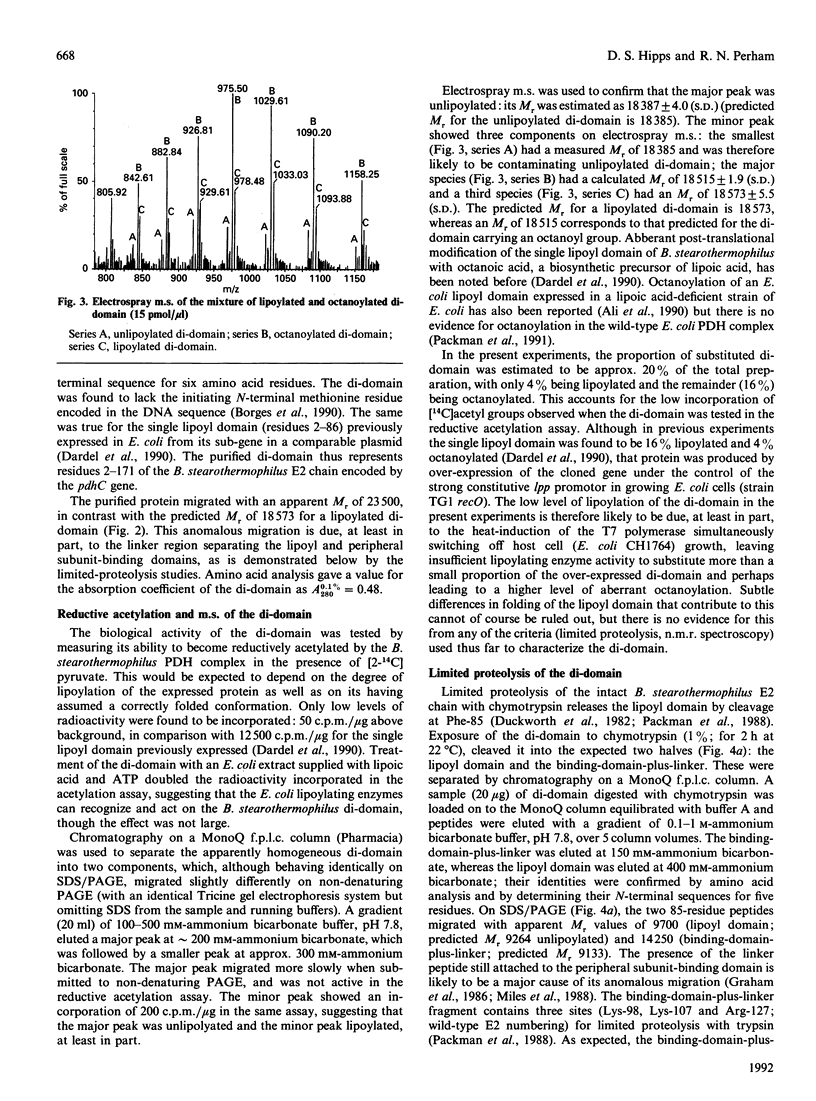
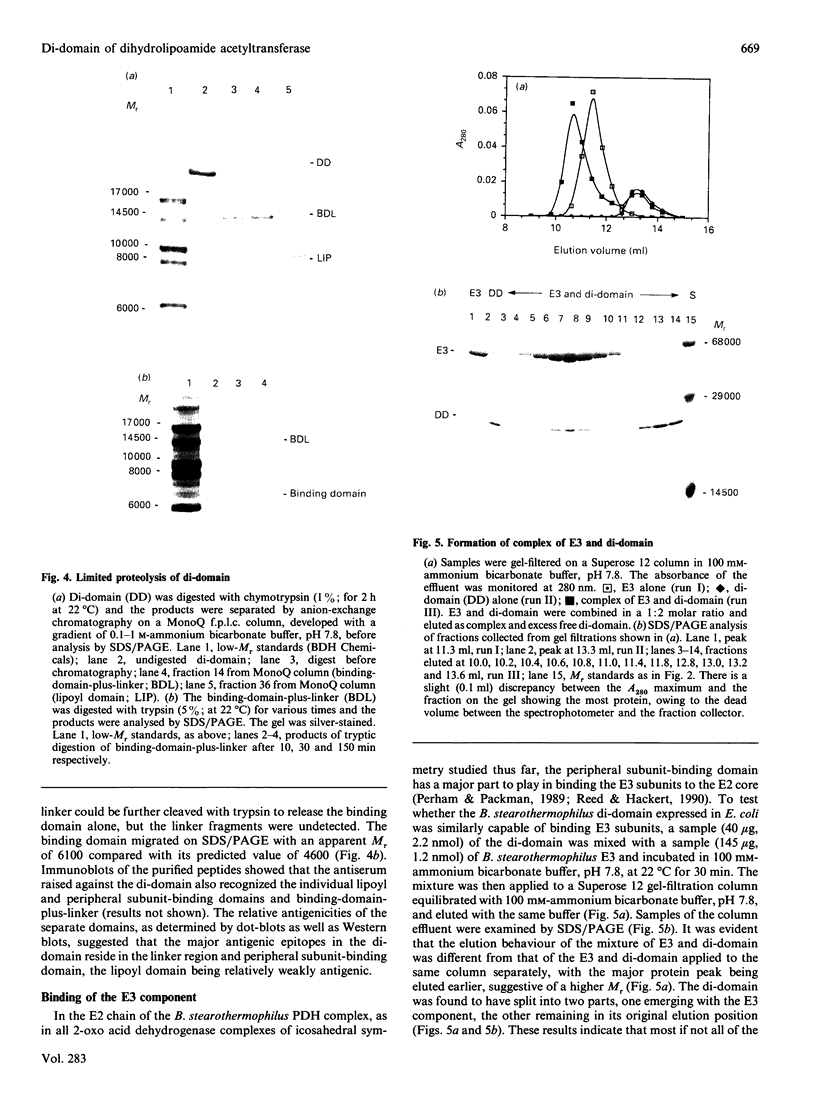
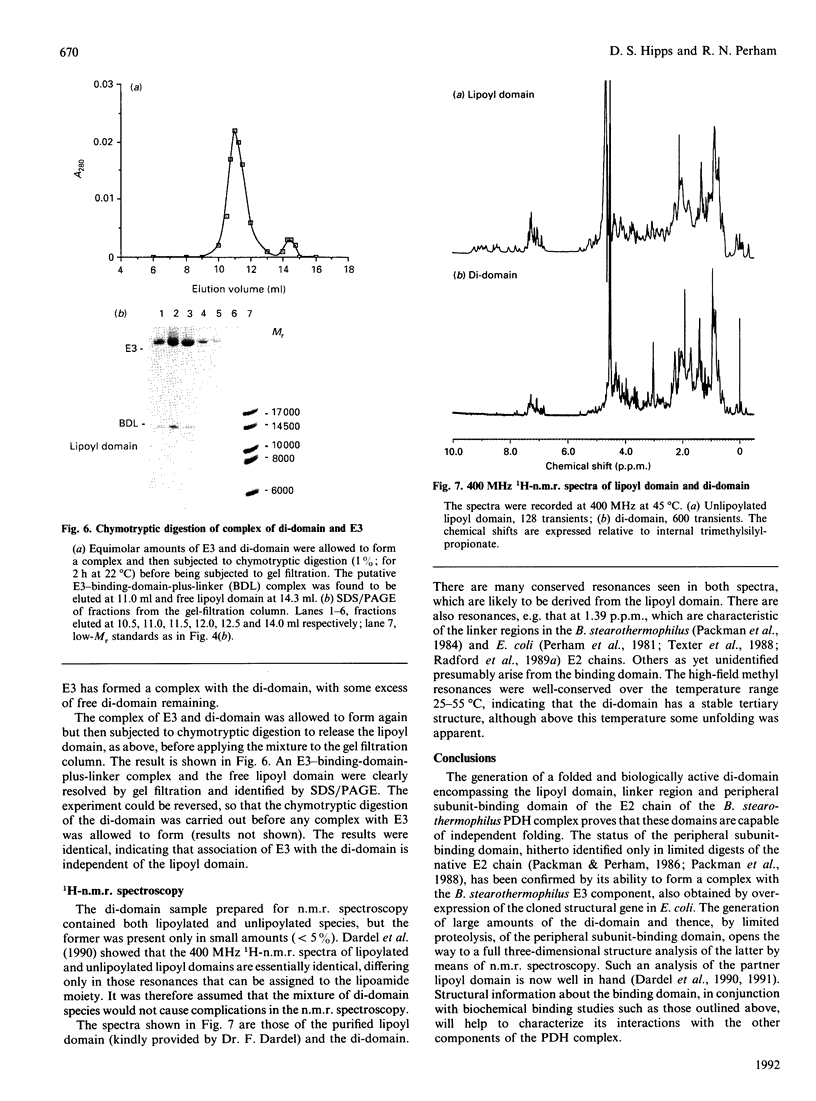
A sub-gene encoding the N-terminal 170 residues of the dihydrolipoamide acetyltransferase chain of the pyruvate dehydrogenase multienzyme complex of Bacillus stearothermophilus was over-expressed in Escherichia coli. The expressed polypeptide consists of the lipoyl domain, inter-domain linker and peripheral subunit-binding domain; these were found to have folded into their native functional conformations as judged by reductive acetylation of the lipoyl domain, limited proteolysis of the linker region and ability to bind the dihydrolipoamide dehydrogenase dimer. The di-domain was largely (80%) unlipoylated; a small proportion (4%) was correctly modified with lipoic acid and the remainder (16%) was aberrantly modified with octanoic acid. A polyclonal antiserum was raised that recognized both the di-domain and the individual component domains. The 400 MHz 1H-n.m.r. spectrum of the di-domain showed resonances corresponding to those seen in spectra of the lipoyl domain, plus others characteristic of amino acid residues in the flexible linker region. Further, as yet unidentified, resonances are likely to be derived from the peripheral subunit-binding domain. The existence and independent folding of the peripheral subunit-binding domain is thus confirmed and its purification in large-scale amounts for detailed structural analysis is now possible.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ali S. T., Moir A. J., Ashton P. R., Engel P. C., Guest J. R. Octanoylation of the lipoyl domains of the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex in a lipoyl-deficient strain of Escherichia coli. Mol Microbiol. 1990 Jun;4(6):943–950. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1990.tb00667.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borges A., Hawkins C. F., Packman L. C., Perham R. N. Cloning and sequence analysis of the genes encoding the dihydrolipoamide acetyltransferase and dihydrolipoamide dehydrogenase components of the pyruvate dehydrogenase multienzyme complex of Bacillus stearothermophilus. Eur J Biochem. 1990 Nov 26;194(1):95–102. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1990.tb19432.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dardel F., Laue E. D., Perham R. N. Sequence-specific 1H-NMR assignments and secondary structure of the lipoyl domain of the Bacillus stearothermophilus pyruvate dehydrogenase multienzyme complex. Eur J Biochem. 1991 Oct 1;201(1):203–209. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1991.tb16275.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dardel F., Packman L. C., Perham R. N. Expression in Escherichia coli of a sub-gene encoding the lipoyl domain of the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex of Bacillus stearothermophilus. FEBS Lett. 1990 May 21;264(2):206–210. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)80249-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duckworth H. W., Jaenicke R., Perham R. N., Wilkie A. O., Finch J. T., Roberts G. C. Limited proteolysis and proton NMR spectroscopy of Bacillus stearothermophilus pyruvate dehydrogenase multienzyme complex. Eur J Biochem. 1982 May;124(1):63–69. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb05906.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham L. D., Packman L. C., Perham R. N. Kinetics and specificity of reductive acylation of lipoyl domains from 2-oxo acid dehydrogenase multienzyme complexes. Biochemistry. 1989 Feb 21;28(4):1574–1581. doi: 10.1021/bi00430a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guest J. R., Angier S. J., Russell G. C. Structure, expression, and protein engineering of the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex of Escherichia coli. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1989;573:76–99. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1989.tb14988.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawkins C. F., Borges A., Perham R. N. Cloning and sequence analysis of the genes encoding the alpha and beta subunits of the E1 component of the pyruvate dehydrogenase multienzyme complex of Bacillus stearothermophilus. Eur J Biochem. 1990 Jul 31;191(2):337–346. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1990.tb19128.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meinnel T., Mechulam Y., Fayat G. Fast purification of a functional elongator tRNAmet expressed from a synthetic gene in vivo. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Aug 25;16(16):8095–8096. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.16.8095. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merril C. R., Goldman D., Sedman S. A., Ebert M. H. Ultrasensitive stain for proteins in polyacrylamide gels shows regional variation in cerebrospinal fluid proteins. Science. 1981 Mar 27;211(4489):1437–1438. doi: 10.1126/science.6162199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miles J. S., Guest J. R., Radford S. E., Perham R. N. Investigation of the mechanism of active site coupling in the pyruvate dehydrogenase multienzyme complex of Escherichia coli by protein engineering. J Mol Biol. 1988 Jul 5;202(1):97–106. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90522-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Packman L. C., Borges A., Perham R. N. Amino acid sequence analysis of the lipoyl and peripheral subunit-binding domains in the lipoate acetyltransferase component of the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex from Bacillus stearothermophilus. Biochem J. 1988 May 15;252(1):79–86. doi: 10.1042/bj2520079. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Packman L. C., Green B., Perham R. N. Lipoylation of the E2 components of the 2-oxo acid dehydrogenase multienzyme complexes of Escherichia coli. Biochem J. 1991 Jul 1;277(Pt 1):153–158. doi: 10.1042/bj2770153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Packman L. C., Perham R. N. Chain folding in the dihydrolipoyl acyltransferase components of the 2-oxo-acid dehydrogenase complexes from Escherichia coli. Identification of a segment involved in binding the E3 subunit. FEBS Lett. 1986 Oct 6;206(2):193–198. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)80979-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Packman L. C., Perham R. N., Roberts G. C. Domain structure and 1H-n.m.r. spectroscopy of the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex of Bacillus stearothermophilus. Biochem J. 1984 Jan 1;217(1):219–227. doi: 10.1042/bj2170219. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel M. S., Roche T. E. Molecular biology and biochemistry of pyruvate dehydrogenase complexes. FASEB J. 1990 Nov;4(14):3224–3233. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.4.14.2227213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perham R. N. Domains, motifs, and linkers in 2-oxo acid dehydrogenase multienzyme complexes: a paradigm in the design of a multifunctional protein. Biochemistry. 1991 Sep 3;30(35):8501–8512. doi: 10.1021/bi00099a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perham R. N., Duckworth H. W., Roberts G. C. Mobility of polypeptide chain in the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex revealed by proton NMR. Nature. 1981 Jul 30;292(5822):474–477. doi: 10.1038/292474a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perham R. N., Packman L. C. 2-Oxo acid dehydrogenase multienzyme complexes: domains, dynamics, and design. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1989;573:1–20. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1989.tb14983.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perham R. N., Packman L. C., Radford S. E. 2-Oxo acid dehydrogenase multi-enzyme complexes: in the beginning and halfway there. Biochem Soc Symp. 1987;54:67–81. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radford S. E., Laue E. D., Perham R. N., Martin S. R., Appella E. Conformational flexibility and folding of synthetic peptides representing an interdomain segment of polypeptide chain in the pyruvate dehydrogenase multienzyme complex of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 15;264(2):767–775. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radford S. E., Perham R. N., Ullrich S. J., Appella E. Antibodies against an inter-domain segment of polypeptide chain inhibit active-site coupling in the pyruvate dehydrogenase multienzyme complex. FEBS Lett. 1989 Jul 3;250(2):336–340. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)80750-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed L. J., Hackert M. L. Structure-function relationships in dihydrolipoamide acyltransferases. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jun 5;265(16):8971–8974. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Coulson A. R., Barrell B. G., Smith A. J., Roe B. A. Cloning in single-stranded bacteriophage as an aid to rapid DNA sequencing. J Mol Biol. 1980 Oct 25;143(2):161–178. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90196-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schägger H., von Jagow G. Tricine-sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis for the separation of proteins in the range from 1 to 100 kDa. Anal Biochem. 1987 Nov 1;166(2):368–379. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(87)90587-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabor S., Richardson C. C. A bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase/promoter system for controlled exclusive expression of specific genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(4):1074–1078. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.4.1074. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor J. W., Ott J., Eckstein F. The rapid generation of oligonucleotide-directed mutations at high frequency using phosphorothioate-modified DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Dec 20;13(24):8765–8785. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.24.8765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor J. W., Schmidt W., Cosstick R., Okruszek A., Eckstein F. The use of phosphorothioate-modified DNA in restriction enzyme reactions to prepare nicked DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Dec 20;13(24):8749–8764. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.24.8749. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Texter F. L., Radford S. E., Laue E. D., Perham R. N., Miles J. S., Guest J. R. Site-directed mutagenesis and 1H NMR spectroscopy of an interdomain segment in the pyruvate dehydrogenase multienzyme complex of Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1988 Jan 12;27(1):289–296. doi: 10.1021/bi00401a044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]