Figure. Pedigree of Australian Family and Segregation of the PURA Variant.
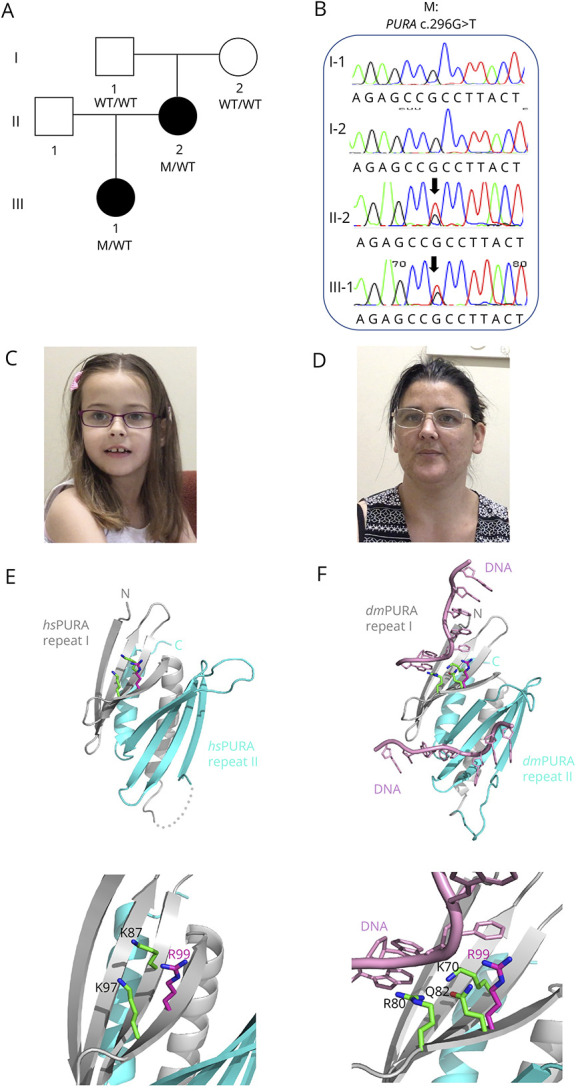
(A) The pedigree of the Australian family showing genotypes based on sequencing analyses. (B) Segregation of PURA c.296G>T (p.Arg99Leu) missense variant by Sanger sequencing. (C and D) Photographs of proband and her mother showing pointed chin and long face. (E) Ribbon model of the nucleic acid–binding domain of human PURA (PDB ID: 8CHT12; amino acids 57–212; repeats I and II shown in grey and cyan, respectively). Side chains of R99 (magenta) and K97 (green) and K87 (green) are shown as sticks. The lower panel in (C) shows magnification of the region of interest. (F) The potential influence of R99 on the interaction with the nucleic acids. The figure shows the X-ray structure of Drosophila PURA (PDB ID: 5FGP13; amino acids 40–183; repeats I and II shown in grey and cyan, respectively) with bound DNA (shown in pink). The amino acids involved in the direct interaction with DNA (K70 and R80) are shown as green sticks. The residue Q82 in Drosophila (green) and its human equivalent R99 (magenta) are shown as well. The position of R99 has been calculated from the superposition of the X-ray structure of human PURA on the Drosophila experimental model. The lower panel in (D) shows magnification of the region of interest.
