Abstract
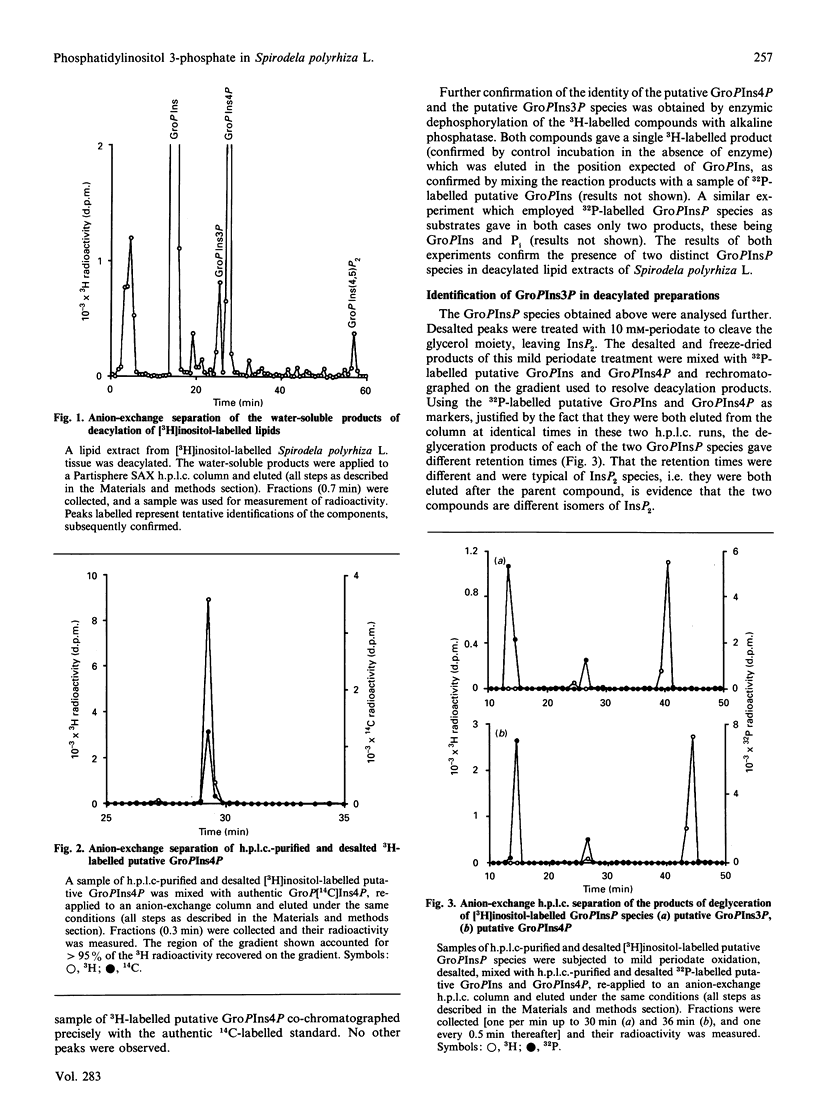
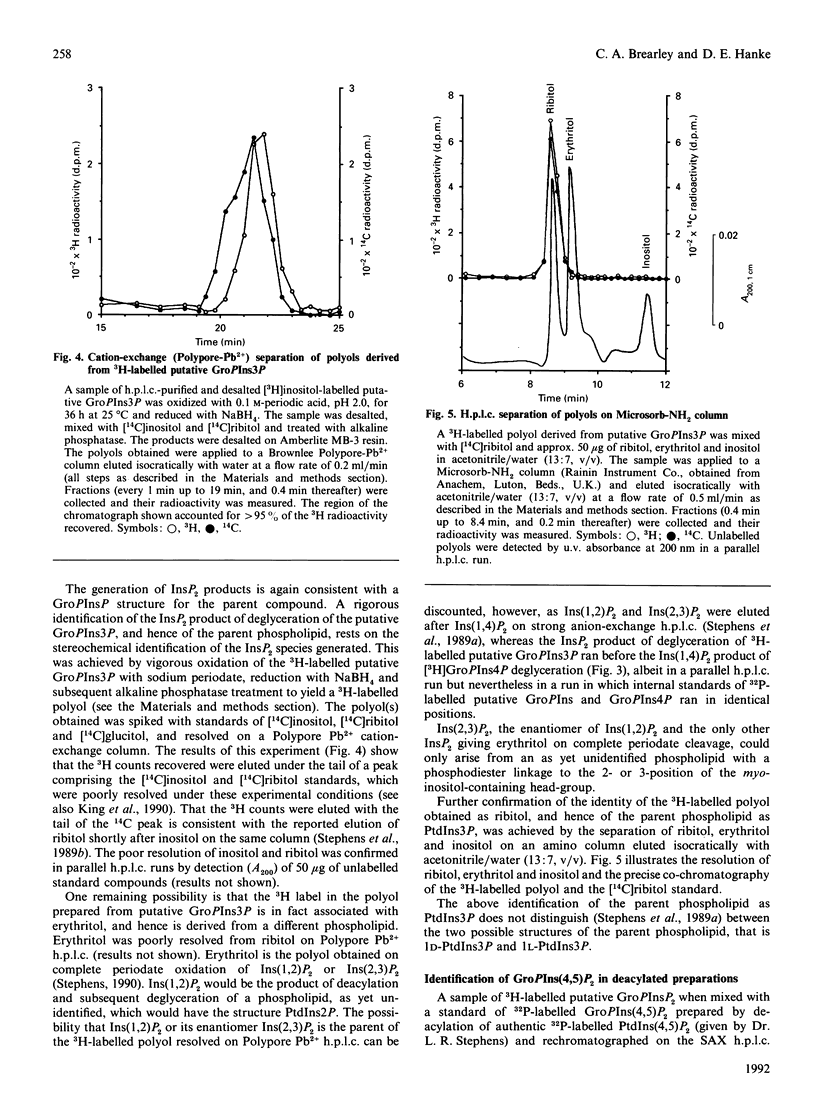
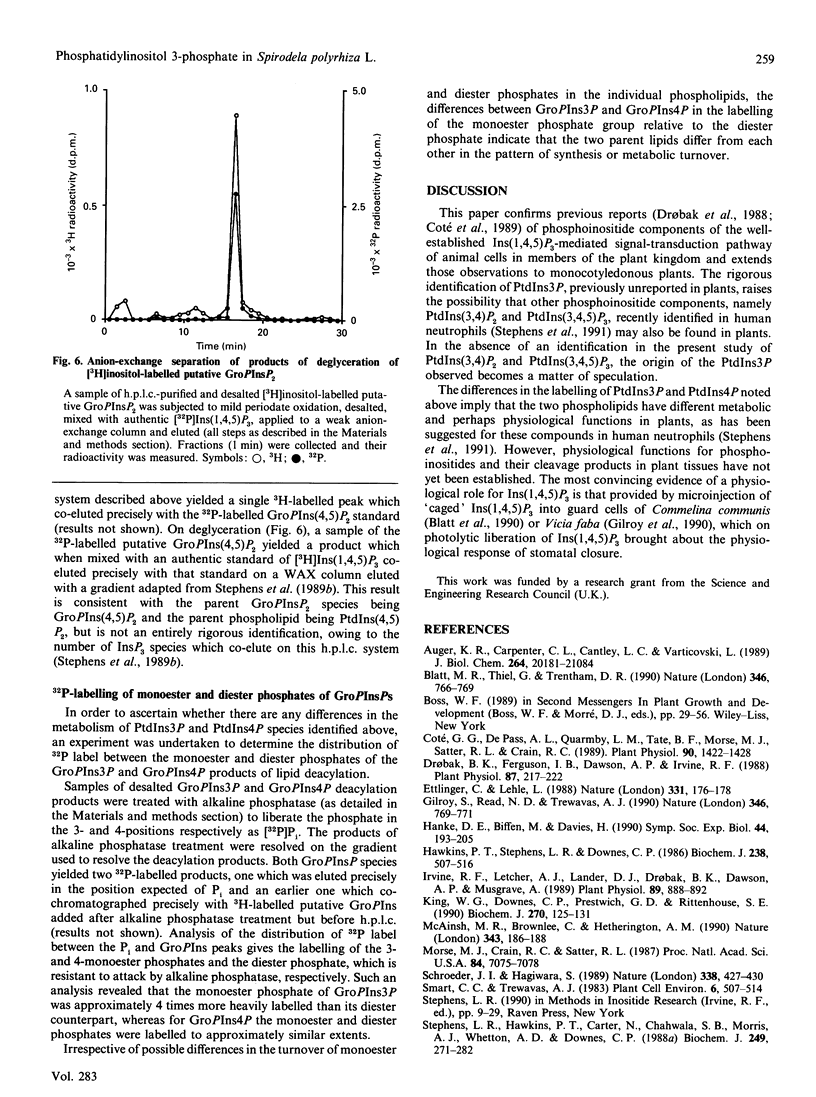
Labelling of Spirodela polyrhiza L. plants with [3H]inositol and [32P]Pi yielded a series of phosphoinositides which were identified as PtdIns, PtdIns4P and PtdIns(4,5)P2. In addition, systematic degradation of a phospholipid extract identified PtdIns3P. Analysis of the distribution of 32P label between the monoester and diester phosphate groups of PtdIns3P and PtdIns4P revealed differences in the labelling of the monoester phosphate, suggesting that the two PtdInsP species are not synthesized or metabolized in a co-ordinate manner.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Auger K. R., Carpenter C. L., Cantley L. C., Varticovski L. Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and its novel product, phosphatidylinositol 3-phosphate, are present in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem. 1989 Dec 5;264(34):20181–20184. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blatt M. R., Thiel G., Trentham D. R. Reversible inactivation of K+ channels of Vicia stomatal guard cells following the photolysis of caged inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate. Nature. 1990 Aug 23;346(6286):766–769. doi: 10.1038/346766a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coté G. G., Depass A. L., Quarmby L. M., Tate B. F., Morse M. J., Satter R. L., Crain R. C. Separation and Characterization of Inositol Phospholipids from the Pulvini of Samanea saman. Plant Physiol. 1989 Aug;90(4):1422–1428. doi: 10.1104/pp.90.4.1422. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drøbak B. K., Ferguson I. B., Dawson A. P., Irvine R. F. Inositol-containing lipids in suspension-cultured plant cells: an isotopic study. Plant Physiol. 1988 May;87(1):217–222. doi: 10.1104/pp.87.1.217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ettlinger C., Lehle L. Auxin induces rapid changes in phosphatidylinositol metabolites. Nature. 1988 Jan 14;331(6152):176–178. doi: 10.1038/331176a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilroy S., Read N. D., Trewavas A. J. Elevation of cytoplasmic calcium by caged calcium or caged inositol triphosphate initiates stomatal closure. Nature. 1990 Aug 23;346(6286):769–771. doi: 10.1038/346769a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanke D. E., Biffen M., Davies H. Phosphoinositides and plant growth substance action. Symp Soc Exp Biol. 1990;44:193–205. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawkins P. T., Stephens L., Downes C. P. Rapid formation of inositol 1,3,4,5-tetrakisphosphate and inositol 1,3,4-trisphosphate in rat parotid glands may both result indirectly from receptor-stimulated release of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate from phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate. Biochem J. 1986 Sep 1;238(2):507–516. doi: 10.1042/bj2380507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irvine R. F., Letcher A. J., Lander D. J., Drøbak B. K., Dawson A. P., Musgrave A. Phosphatidylinositol(4,5)bisphosphate and Phosphatidylinositol(4)phosphate in Plant Tissues. Plant Physiol. 1989 Mar;89(3):888–892. doi: 10.1104/pp.89.3.888. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King W. G., Downes C. P., Prestwich G. D., Rittenhouse S. E. Ca2(+)-stimulatable and protein kinase C-inhibitable accumulation of inositol 1,3,4,6-tetrakisphosphate in human platelets. Biochem J. 1990 Aug 15;270(1):125–131. doi: 10.1042/bj2700125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morse M. J., Crain R. C., Satter R. L. Light-stimulated inositolphospholipid turnover in Samanea saman leaf pulvini. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(20):7075–7078. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.20.7075. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens L. R., Hawkins P. T., Barker C. J., Downes C. P. Synthesis of myo-inositol 1,3,4,5,6-pentakisphosphate from inositol phosphates generated by receptor activation. Biochem J. 1988 Aug 1;253(3):721–733. doi: 10.1042/bj2530721. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens L. R., Hawkins P. T., Downes C. P. An analysis of myo-[3H]inositol trisphosphates found in myo-[3H]inositol prelabelled avian erythrocytes. Biochem J. 1989 Sep 15;262(3):727–737. doi: 10.1042/bj2620727. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens L. R., Hawkins P. T., Morris A. J., Downes P. C. L-myo-inositol 1,4,5,6-tetrakisphosphate (3-hydroxy)kinase. Biochem J. 1988 Jan 1;249(1):283–292. doi: 10.1042/bj2490283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens L. R., Hughes K. T., Irvine R. F. Pathway of phosphatidylinositol(3,4,5)-trisphosphate synthesis in activated neutrophils. Nature. 1991 May 2;351(6321):33–39. doi: 10.1038/351033a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens L., Hawkins P. T., Carter N., Chahwala S. B., Morris A. J., Whetton A. D., Downes P. C. L-myo-inositol 1,4,5,6-tetrakisphosphate is present in both mammalian and avian cells. Biochem J. 1988 Jan 1;249(1):271–282. doi: 10.1042/bj2490271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens L., Hawkins P. T., Downes C. P. Metabolic and structural evidence for the existence of a third species of polyphosphoinositide in cells: D-phosphatidyl-myo-inositol 3-phosphate. Biochem J. 1989 Apr 1;259(1):267–276. doi: 10.1042/bj2590267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitman M., Downes C. P., Keeler M., Keller T., Cantley L. Type I phosphatidylinositol kinase makes a novel inositol phospholipid, phosphatidylinositol-3-phosphate. Nature. 1988 Apr 14;332(6165):644–646. doi: 10.1038/332644a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


