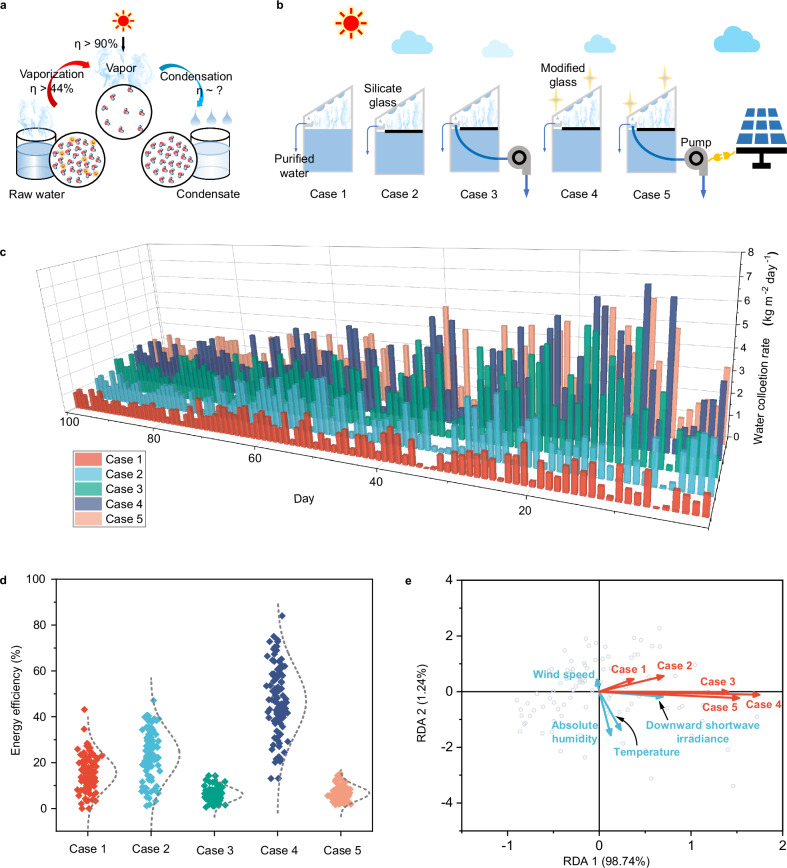
Fig. 2. Outdoor evaluation of solar-to-water conversion in solar water evaporation (SWE) devices.
a The solar-to-vapor processes and the corresponding energy efficiency. b Schematic diagram of case 1–5 SWE devices. Case 1 is a reference system without solar evaporators. Case 2 includes solar evaporators. Case 3 further pumps vapor out through a condensing tube for forced condensation with additional photovoltaics. Case 4 uses coated glass (condensation-enhanced) to condense the water without external energy input. Case 5 integrates both the condensing tube (powered by photovoltaics) and condensation-enhanced glass for condensation. c Daily safely managed drinking water (SMDW) yield of all cases during a 100-day successive pilot study. d Statistical distribution of the solar energy utilization efficiency of all cases. e Redundancy analysis (RDA) between the meteorological parameters and the SMDW yield.