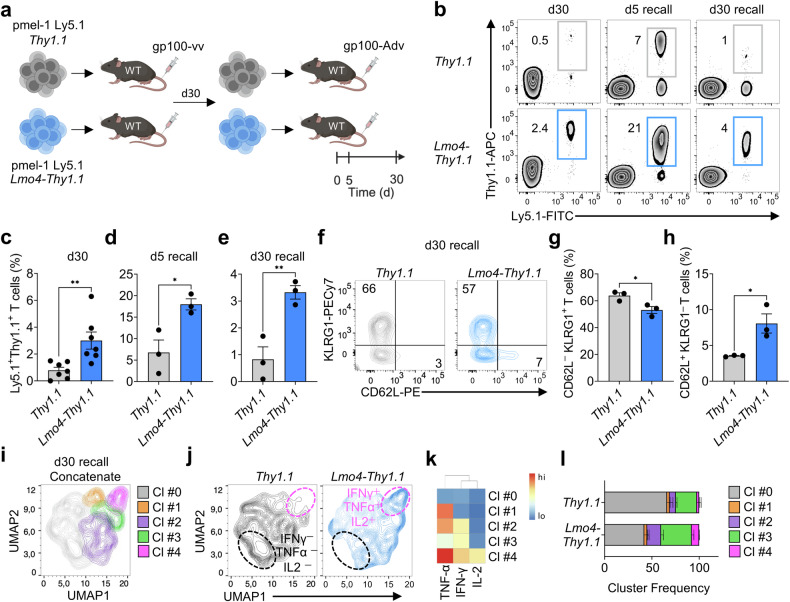
Fig. 2.
Increased expression of Lmo4 augments CD8+ T cell recall responses. a Experimental design investigating the impact of Lmo4 overexpression on CD8+ T cell secondary responses. b–e Flow cytometry analysis (b) and percentages (c–e) of splenic pmel-1 CD8+ T cells following transfer of either 105 pmel-1 Ly5.1+ Thy1.1+ or Lmo4-Thy1.1+ CD8+ T cells into wild-type mice infected with gp100-vv (primary infection) or gp100-Adv (secondary infection). Assessment was conducted at various time points: d30 after primary infection and d5 or d30 after secondary infection (recall); with seven mice per group for d30 and three mice per group for d5 recall and d30 recall. f–h Flow cytometry analysis (f) and percentages of CD62L−KLRG1+ (g) and CD62L+KLRG1− (h) splenic pmel-1 T cells 5 d after transfer as in (b–e). i UMAP plot of concatenated Thy1.1+ and Lmo4-Thy1.1+ pmel-1 CD8+ T cells isolated from spleens 30 d after secondary transfer as in (b–e) showing the distribution of clusters (Cl) identified by FlowSOM. j UMAP plot of Thy1.1+ and Lmo4-Thy1.1+ pmel-1 CD8+ T cells showing differences in cluster distributions. k Heatmap showing the relative expression levels of indicated cytokines in the FlowSOM clusters. l Bar plot of Thy1.1+ and Lmo4-Thy1.1+ pmel-1 CD8+ T cells isolated from spleens 5 d after treatment as in (b–e) quantifying the distribution of clusters assessed by FlowSOM. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 (unpaired two-tailed Student’s t-test). (a) was created with BioRender.com