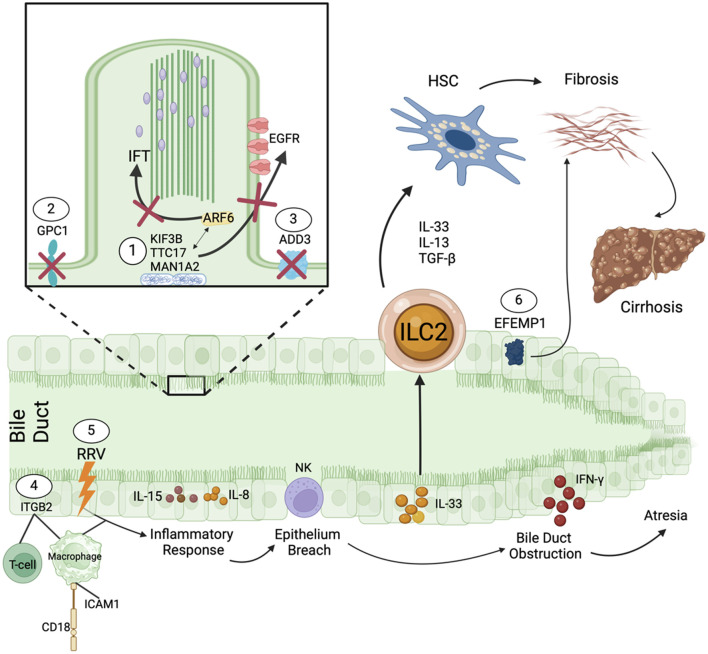
Fig. 3. Effects of specific mutations involved in the development of biliary atresia.
(1) Mutations in KIF3B, TTC17, MAN1A2 and ARF6 result in the inhibition of recruitment of IFTs and EGFRs disrupting normal cilia function.20,22,24 (2) Defective GPC1 alters glypican, which attaches to the apical cell membrane of cholangiocytes, altering cell division and growth.21 (3) ADD3 encodes adducins that play a role in remodeling biliary epithelial junctions. Defects lead to disordered development.21 (4) Mutations in ICAM1, a ligand for CD18 and macrophages, and ITGB2, a ligand for T-cells and macrophages, upregulate an inflammatory response in the bile duct.20,25,26 (5) Likewise, a trigger such as rotavirus type A infection stimulates the production of IL-15 and IL-8. NK cells promote cholangiocyte injury and disrupt the duct epithelium. IL-33 is then secreted, attracting ILC2, which triggers the HSC activation mediated by chemokines and TGF-ß. Activated HSCs lead to hepatic fibrosis and cirrhosis. INF-γ promotes bile duct obstruction and eventual biliary atresia by causing a prominent lymphocytic infiltration.18,19 (6) EFEMP1 encodes a secreted extracellular protein implicated in extracellular matrix remodeling promoting hepatic fibrosis.23 ADD3, adducing-3; ARF6, ADP-ribosylation factor 6; EFEMP1, EGF containing fibulin extracellular matrix protein 1; EGFR, endothelial growth factor receptor; GPC1, glypican-1; HSC, hepatic stellate cell; ICAM1, intercellular adhesion molecule 1; IFTs, intraflagellar transporters; IL, interleukin; ILC2, innate lymphoid cells; INF-γ, interferon-gamma; ITGB2, integrin subunit beta 2; KIF3B, kinesin family member 3B; MAN1A2, mannosidase alpha class 1A member 2; NK, natural killer; RRV, rotavirus type A; TGF-ß, transforming growth factor beta; TTC17, tetratricopeptide repeat domain 17. Adapted with permission from Asai et al., Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2015.