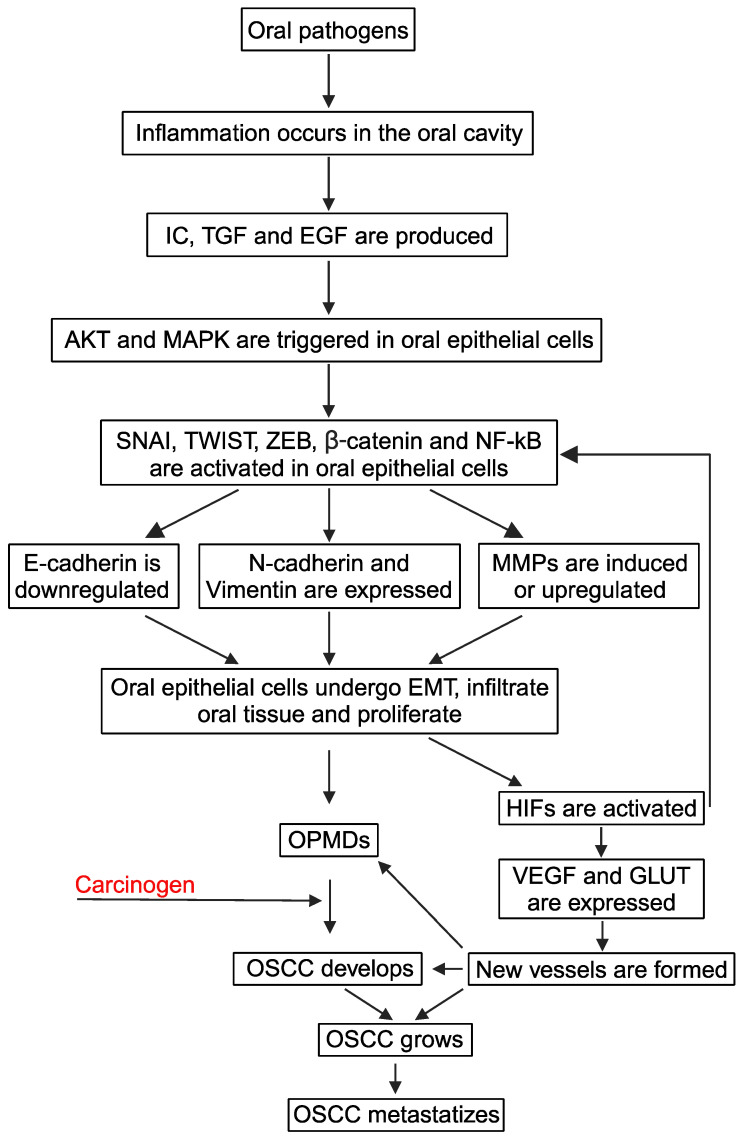
Figure 1.
Molecular mechanisms leading to EMT in oral mucosa. Arrows symbolize directions of connections. Abbreviations: AKT, protein kinase B; E-cadherin, epithelial-cadherin; EGF, epidermal growth factor; EMT, epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition; GLUT, glucose transporter protein; HIF, hypoxia-inducible factor; IC, inflammatory cytokines; MAPK, mitogen-activated protein kinase; MMPs, matrix metalloproteinases; N-cadherin, neuronal-cadherin; NF-κB, nuclear factor kappa B; OPMDs, oral potentially malignant disorders; OSCC, oral squamous cell carcinoma; SNAI, zinc finger snail homolog; TGF, transforming growth factor; TWIST, basic helix–loop–helix twist homolog; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor; ZEB, zinc finger E-box-binding homeobox. Created with BioRender.com.