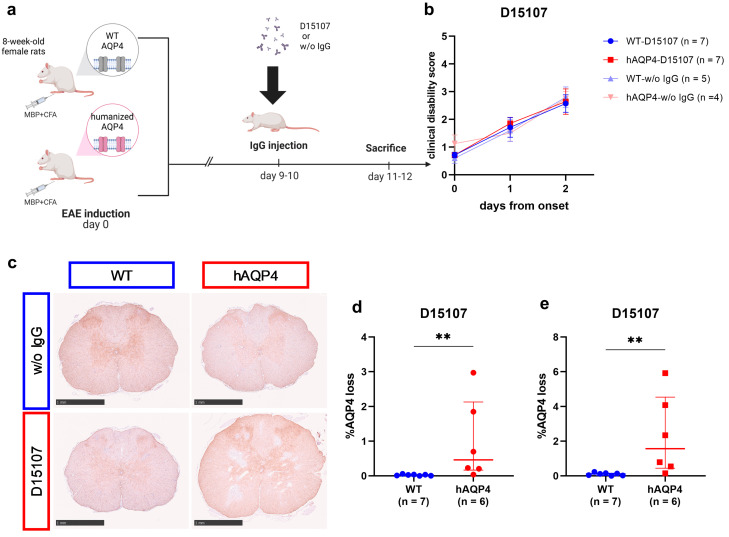
Figure 1.
Human AQP4-specific monoclonal antibody D15107 induced astrocyte damage specifically in hAQP4 rats. (a) Summary of the experimental protocol. Created with BioRender.com. (b) Clinical disability scores of the wild-type Lewis (WT) rats transferred with D15107 (WT-D15107, blue), humanized-aquaporin-4-expressing (hAQP4) rats transferred with D15107 (hAQP4-D15107, red), WT rats without IgG injection (WT-w/o IgG, light blue), and hAQP4 rats without IgG injection (hAQP4-w/o IgG, light red) group on the day of IgG injection (day 0) and after 2 days. Values are mean ± SEM of each group. (c–e) Sizes of AQP4 loss lesions in the spinal cord induced by human AQP4-specific monoclonal antibody on the pathological examination. The percentage of the AQP4 loss area was calculated for 12 slices per rat by dividing the AQP4 loss area by the whole section area. (c) AQP4 staining of the spinal cord sections in each group. Each scale bar = 1 mm. (d) Average of 12 slices per rat in the WT-D15107 and hAQP4-D15107 groups. Values are median ± IQR with individual points. (e) The average percentage of the AQP4 loss area in the slices with the three largest lesions per rat in the WT-D15107 and hAQP4-D15107 groups. Values are median ± IQR with individual points. Statistical analyses were performed using the Wilcoxon test with GraphPad Prism 8.4.3, and significance is indicated as ** p < 0.01.