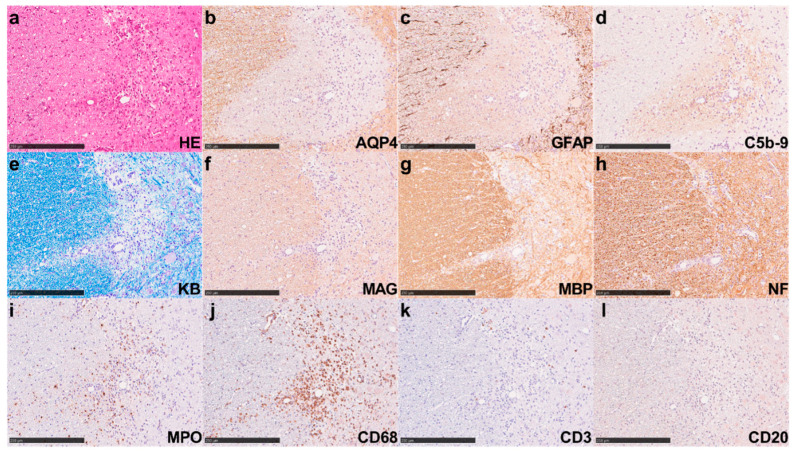
Figure 3.
NMOSD patient-derived IgGs induced severe NMOSD-like lesions in hAQP4 rats. Pathological findings in the spinal cord of hAQP4 rats that received 20 mg of NMO2-IgG. (a) Hematoxylin and eosin (HE) staining showed vasculocentric tissue-destructive lesions. (b,c) Immunohistochemistry (IHC) for AQP4 (b) and glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) (c) revealed complete loss of AQP4 and GFAP, indicating astrocyte damage. (d) IHC for C5b-9 showed vasculocentric complement depositions in the lesion. (e) Klüver–Barrera (KB) staining indicated obvious demyelination in the center of the lesion. (f,g) The IHC for myelin-associated glycoprotein (MAG) (f) and myelin basic protein (MBP) (g) showed a decrease in staining. (h) The IHC for neurofilament (NF) showed mild axonal swelling. (i,j) The IHC for myeloperoxidase (MPO) (i), expressed mostly in neutrophils, and CD68 (j), expressed mainly in macrophage/microglia, revealed marked infiltration by these cells in the lesion. (k,l) The IHC for T-cell marker CD3 (k) and B-cell marker CD20 (l) showed rare infiltration by these cells in the lesion. All these staining procedures were performed using serial sections. All these figures indicate the same lesion. Scale bar = 250 µm.